Configuring Site-to-Site VPN with Forefront TMG and Cisco PIX and ASA
Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 supports several protocols for establishing a site-to-site (LAN to LAN) VPN, including PPTP, L2TP, and IPsec. Of these, IPsec is the only supported protocol for establishing site-to-site VPN connections with third-party VPN devices such as Cisco PIX and ASA. In this post I will demonstrate how to configure Forefront TMG and the Cisco PIX/ASA to create a site-to-site VPN for the following branch office deployment scenario:
[Note: Site-to-site VPN in TMG is supported only in multi-homed network configurations. The TMG firewall must be configured with a minimum of two network interfaces to function as a site-to-site VPN gateway.]
Configuring the TMG Firewall
Open the TMG management console and highlight the Remote Access Policy (VPN) node in the navigation tree, then select the Remote Sites tab in the main window. In the Tasks pane on the right side, click Create VPN Site-to-Site Connection.

The Site-to-Site Connection Wizard will collect the necessary information to establish the VPN tunnel. Enter a descriptive name when prompted.
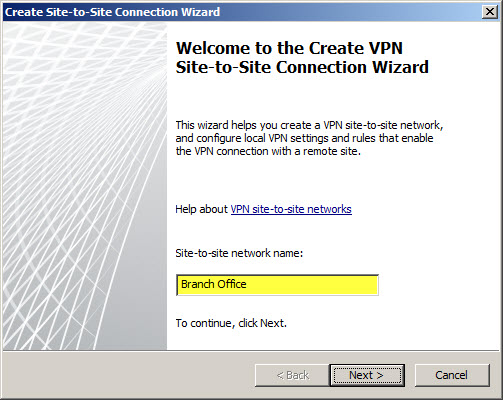
Select IP Security protocol (IPsec) tunnel mode.

If the TMG firewall is a member of an array that does not have Network Load Balancing (NLB) enabled, select a node to be the connection owner. If NLB is enabled, the connection owner is assigned automatically. [Note: When configuring a site-to-site VPN connection on a TMG firewall that is a member of an array and NLB is not enabled, hosts that are accessed via the tunnel must be configured with a default gateway or static route that will direct traffic back to the array member chosen as the connection owner.]

Enter the IP addresses of the remote and local VPN gateways. The remote VPN gateway IP address will be the IP address assigned to the outside network interface on the Cisco PIX/ASA firewall. The local VPN gateway IP address will be the IP address assigned to the External network interface on the TMG firewall. If the TMG firewall is part of an NLB-enabled array, specify the Virtual IP (VIP) address assigned to the External network of the array.

Certificates are the most secure and preferred method for authenticating tunnel endpoints, but because they are more complex and difficult to configure, many security administrators opt instead to use pre-shared keys. When choosing a key, be sure it is very long and complex (up to 128 characters – it is a good idea to use a random password generator for this task). Although using special characters is an excellent idea for complex keys, avoid using the question mark as the PIX and ASA object to this.

Add the address range(s) of the remote site network(s). It is recommended that these addresses be configured along subnet boundaries.
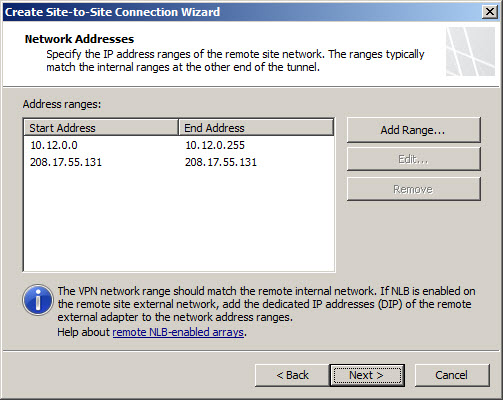
A network relationship needs to be established between the Internal network and the remote site network. The wizard automatically establishes a route relationship between these two networks.

An access rule is required to allow communication between the Internal network and the remote site network. If this is a fully trusted remote network (e.g. branch office), select all outbound traffic. If the remote network is untrusted (e.g. business partner), specify which protocols and ports are allowed.
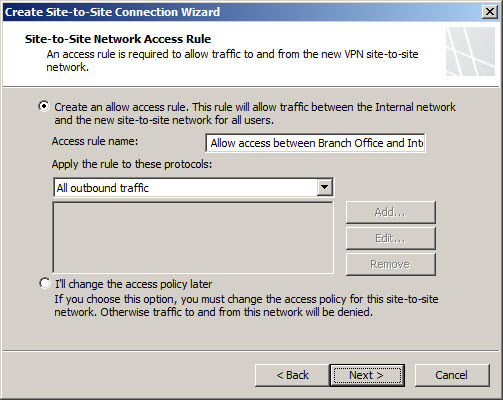
Review the configuration and select Finish.

Do not apply the configuration now. The default encryption settings chosen by TMG are incompatible with the Cisco PIX and ASA. To change these settings to match the settings on the PIX/ASA, right-click the remote site and choose properties. Choose the Connection tab and then click IPsec Settings.
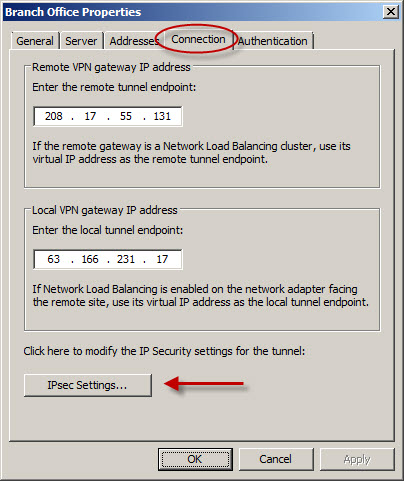
For the Phase I settings, change the Encryption algorithm to 3DES, the Integrity algorithm to SHA1, and the Authenticate and generate a new key every: to 86400 seconds (24 hours).
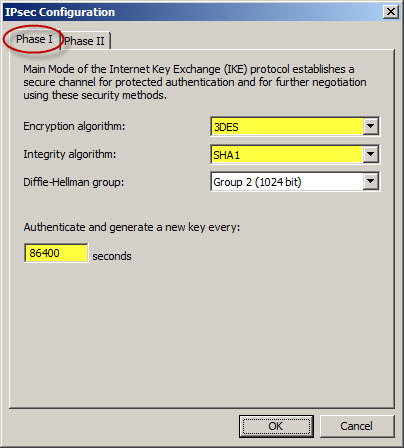
For the Phase II settings, change the Encryption algorithm to 3DES and the Integrity algorithm to SHA1. Change the Session key settings so that a new key is generated every 4608000 Kbytes or 28800 seconds (8 hours).
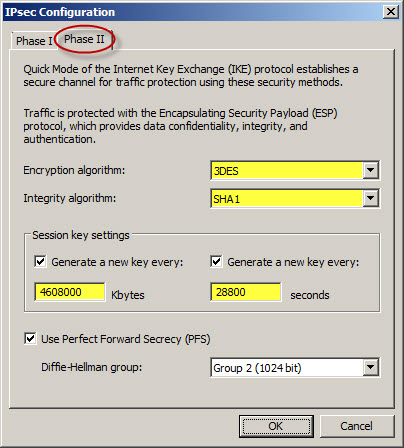
Once complete, save and apply the changes.
Configuring the Cisco ASA 7.x
Connect to the ASA with administrative privileges and enter enable mode. To configure the management connection (phase 1) parameters, establish an ISAKMP policy and set the parameters to use a pre-shared key, use 3DES/SHA for encryption and integrity, specify the use of Diffie-Hellman group 2 (1024-bit) and authenticate and generate a new key every 86400 seconds (24 hours).
crypto isakmp policy 10 authentication pre-share encryption 3des hash sha group 2 lifetime 86400 crypto isakmp enable outside
Configure a tunnel-group for the remote peer and establish authentication using a pre-shared key.
tunnel-group 63.166.231.17 type ipsec-l2l tunnel-group 63.166.231.17 ipsec-attributes pre-shared-key mMWsT0umh_UQmh]yevjNBW_F
For the data connection (phase 2) create an access rule that defines which traffic to protect using this tunnel. In this example, create an access rule that defines all IP traffic going from 10.12.0.0/24 to 172.16.1.0/24.
access-list branch_office extended permit ip 10.12.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
Create a NAT rule to exempt any traffic matching this access rule from NAT.
nat (inside) 0 access-list branch_office
Define which encryption algorithms will be used to protect this traffic. In this example specify the use of 3DES and SHA1.
crypto ipsec transform-set branch_office esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Build the crypto map, indicating that any traffic that matches the branch_office ACL is sent to the specified remote peer using the encryption algorithm defined in the brach_office transform set with Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) enabled using Diffie-Hellman Group 2.
crypto map branch_office_map 1 match address branch_office crypto map branch_office_map 1 set pfs group2 crypto map branch_office_map 1 set peer 63.166.231.17 crypto map branch_office_map 1 set transform-set branch_office
Activate the crypto map on the ASA’s outside interface.
crypto map branch_office_map interface outside
Configuring the Cisco PIX 6.x
Creating a site-to-site VPN connection on a Cisco PIX is similar but slightly different than configuring an ASA. For example, when configuring the management connection (phase 1) parameters using the same configuration used previously, use the following commands:
crypto isakmp policy 10 authen pre-share crypto isakmp policy 10 encrypt 3des crypto isakmp policy 10 hash sha crypto isakmp policy 10 group 2 crypto isakmp policy 10 lifetime 86400 crypto isakmp key mMWsT0umh_UQmh]yevjNBW_F address 63.166.231.17 netmask 255.255.255.255 crypto isakmp enable outside
Create the access rule defining which traffic to protect using this tunnel.
access-list branch_office permit ip 10.12.0.0 255.255.255.0 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0
Exempt this traffic from NAT.
nat (inside) 0 access-list branch_office
Protect this traffic using 3DES and SHA1.
crypto ipsec transform-set branch_office esp-3des esp-sha-hmac
Build the crypto map.
crypto map branch_office_map 1 ipsec-isakmp crypto map branch_office_map 1 match address branch_office crypto map branch_office_map 1 set peer 63.166.231.17 crypto map branch_office_map 1 set transform-set branch_office crypto map branch_office_map 1 set pfs group2
Activate the crypto map on the PIX outside interface.
crypto map branch_office_map interface outside
Unlike the ASA, the PIX requires an access rule to allow tunneled traffic to cross the firewall. For the branch office scenario (fully trusted network), allow all IP traffic from the 172.16.1.0/24 network to reach the 10.12.0.0/24 network and assign that access rule to the outside interface.
access-list main_office_in permit ip 172.16.1.0 255.255.255.0 10.12.0.0 255.255.255.0 access-group main_office_in in interface outside
Due to formatting issues, some of the text in the PIX and ASA command examples may be truncated. You can download the script files for these examples here: PIX | ASA.






Hello Richard!
This topic is right good and useful, I also wanted to process, however, due to technical problems with equipment and testing I am unable to, but in any case subject is useful and instructive.
Thanks
Best Regards
Thanks Ahmet!
hi
any way you can do a article on connecting a site to site vpn with a netgear vpn gateway
i get my vpn connected on both sides (netgear and tmg) but am unable to transfer or even ping between the sites. nothing even shows in the tmg log for this
I don’t have any experience with Netgear VPN gateways, nor do I have any hardware to test with unfortunately.
Hi Richard,
we need to create a VPN site-to-site with a business partner, between our TMG and their GateProtect FW. When we configure the network on the TMG the e-Mail Traffic to the Business Partner is Denied from the enterprise default rule. Configuring the remote network the IP Adress from their Mail Server is in a network different than the external, where the SMTP traffic goes. Is there a metod to resolve this case?
Thanks
Franco
Thank you very much for this post. Do you have an configuration on Cisco router (not ASA or PIX)? Thanks.
Hi Franco,
I would look closely at your access rules. If you are being denied by the default rule, no other access rule matched. With regard to the remote network configuration, TMG needs to know which specific subnets are reachable via this tunnel, so you’ll need to make sure that any subnets at your business partner are included in your TMG site-to-site VPN network configuration.
I’m sorry, I do not. Unfortunately I don’t have a Cisco router in my test lab.
Thanks! It’s very useful article… as usual on this site… Best regards
Thanks for the kind words. Glad you found the information helpful! 🙂
Nice article! But I’ve a question… If the remote site have a load balance/failover device in front of TMG and that device is in fact de remote VPN gateway, how show I configure TMG to use two public IP address so I can make use of the failover VPN feature?
You can assign multiple IP address to the external network interface on TMG and speficy those as your peer IP addresses on the PIX or ASA.
Very nice article. I followed this very detailed and helpful instruction and successfully brought up the VPN tunnel between a remote site with 2 TMG servers running in NLB and an ASA at the main office. However, I am finding that the tunnel is flapping up and down constantly. It stays up only for 30 seconds to 5 minutes, then it goes down, then it re-establishes itself again.
Two Questions:
1. Is there anything that I should do differently if each of the TMG servers in NLB has a dedicated public IP address (in addition to 1 primary virtual public IP and several other public virtual IP addresses)?
2. Is perfrect forward secrecy required for VPN between ASA and TMG to work?
Thanks
Thanks for the kind words. 🙂 There are many things that could cause the tunnel to go up and down. I’d look closely at your networking configuration (routers, switches, etc.) to make sure everything looks healhty there. Often intermediary devices will enforce really short TCP session timeouts which can cause issues. Obviously excessive packet loss can contribute to this as well. As for the NLB question, configure the NLB VIP as the peer IP address. NLB will then assign the connection to one array member. If that array member goes offline, NLB will re-establish the connection on another array member. PFS is not required for VPN between Cisco ASA and the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall, but it is recommended.
Hi Richard,
We have a ASA to TMG VPN that is estblishing Phase 2, and l can see the traffic coming from the ASA (packets encrypted on the ASA) and hitting the Cisco switch behind the TMG and returning, but NO packets being decrypted on the ASA on the return path.
Can you let me know how to debug the TMG to make sure packets are being encypted/decrypted on the incoming and return path.
Thanks.
Hi James,
If the IPsec monitor on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall indicates that phase 2 negotiation was successful, I’d expect this to be an ACL issue on either the TMG or the ASA. Take a close look at the access logs on each…hopefully that will yield some clues.
Thanks!
Hi Richard,
I’ve done the cunfiguration. Everything works well ping, RDP, exept access from network behind TMG to web-server located behind ASA.
I checked ASA access-list and TMG firewall rules, maybe you have some suggestions?
I’d take a close look at the access logs to start. You may even need to drop down and look at the packets using a protocol analyzer to determine where your traffic is getting dropped.
Hi Richard,
Great article! I am having problems with a TMG/Cisco IPSEC tunnel dropping every 4-6 minutes. I am on the Cisco side of the tunnel. When I receive interesting traffic from the TMG the tunnel comes up and an ipsec SA is established. But the next traffic that comes from the TMG tries to establish another SA instead of connecting to my host. When my Cisco receives this second SA request it’s dead peer detection kicks in sends packets back to the TMG. The TMG does not respond to the DPD request and the tunnel drops. Any ideas?
Thanks!
I’m not as experienced with the Cisco ASA side of the tunnel, but that is certainly unusual behavior. If you’re confident that the configuraiton is correct on both sides, you will probably have to break out the protocol analyzer and see what’s going on at the packet level.
I’m experiencing the same problem as Bill, but in my scenario I’ve a SonicWALL instead of a Cisco ASA. It look likes the DPD is not working on the TMG side, and the only way to keep the VPN active is using a machine behind the TMG and ping every 1 min for exemple the private IP address of the SonicWALL (or a machine behind it).
Would this not be expected behavior? The site-to-site VPN is essentially an on-demand network connection, so if there is no interesting traffic passing through the tunnel there’s not need for it to stay up, correct?
In my understanding, and correct me if I’m wrong, DPD is an KeepAlive method to detect the lost of connection to the other end (mainly for failover configurations), not the inactivity of it. But I think the problem is that the TMG is not responding to those maintenance packets as it should. I’ve already tested out the SonicWALL with others IPSec vendors and some UTM’s softwares and worked out pretty well, so I’m assuming that the problem is in TMG.
I’m unfamiliar with DPD, and I’m pretty confident that TMG doesn’t support it. I’ve certainly never seen anything like that when configuring site-to-site VPN with Forefront TMG 2010 anyway.
Hey guys, have a look at this blog post from the Forefront TMG 2010 team. Looks like the issue documented there is similar to what you are seeing with site-to-site VPN. I’d be very interested to know if applying the hotfix they mention resolves your issue.
Hi
I have a cisco 1841Router , where I have to configure a VPN….. what will be change in commands
Hi! Great article! We have successfully created a site-to-site VPN between our TMG and a branch office using a Cisco ASA, and this article saved us a large amount of time and frustration. But, as mentioned in the article, it works only with 3DES and SHA1. Has there been any development recently regarding better encryption level, like AES256 / SHA256? It seems like both systems support it.
Since I’m not a Cisco expert I’m not sure. My experience is limited to Cisco PIX and ASA firewalls. The principles should be the same I would expect.
Not to my knowledge… 😦
Great article. I have a TMG 2010 connected to 2 ISP’s. I have a IPSEC tunnel going to an ASA box. How would I configure the TMG side to be able to switch the tunnel traffic to ISP2 when ISP1 goes down. The ISP’s have given me public ip addresses that have different subnet/network ID’s.
To my knowledge there is no way to do this automatically with Forefront TMG 2010 when configured with two ISPs. Although TMG will attempt to reestablish the connection to the remote peer if an ISP is not available, the problem lies on the Cisco ASA side. If an ISP fails, TMG will have to be reached via a different IP address, which will require a new tunnel to be configured and enabled on the Cisco ASA.
Hi Richard,
We have followed your steps to create site to site VPN without NLB. It worked fine on one TMG server. We thought why not create another server with same settings for a backup purpose if first one fails by some reason.
Now, when I come to step “”Add the address range(s) of the remote site network(s). It is recommended that these addresses be configured along subnet boundaries.”” on another server it gives me below error
“The internal network includes IP addresses in the range x.x.x.x – x.x.x.x”. Networks cannot contain IP addresses that overlap with another network.
here x.x.x.x you may consider ip 208.17.55.131 as an example as our external gateway ip.
Why this behavior? Any idea?
Be sure you are specifying the VIP of the remote site tunnel endpoint. More details here…
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd441067.aspx
Hi Richard,
I have a site-to-site to a Cisco ASA per your article but the TMG cant ping the Cisco or ping a device in the remote network. A server behind the TMG can ping a device behind Cisco so the tunnel is UP. Also a server behind Cisco cant ping the TMG.
So, the first part of your question is expected behavior I believe. As for the server behind Cisco not being able to ping TMG, this is also expected as ICMP should be dropped by ACL on TMG.
Hi Richard,
I’ve recently moved my working site-to-site links from our ISA 2006 servers to a NLB TMG 2010 array installed on Windows Server 2008R2. I’m currently only running TMG SP1 rollup 2 (I think). Since adding the site-to-site connections I see a lot of the following errors in my alerts tab:
The Firewall service cannot remove the IPsec configuration for S2S Network network.
The failure is due to error: The parameter is incorrect.
Sometimes the connection will work, and then others not. I’ve been through the MS known bug you linked above but I’m not seeing the same symptoms, where the tunnel tries to send the traffic down the wrong public IP address.
Do you know of a solution for the above error message?
I’ve not encountered that specific error before, so I apologize I don’t have much advice for you here. However, a good place to start is to remove all of your site-to-site configuring on your Forefront TMG 2010 and ISA firewalls, then apply the latest service pack and hotfix rollup. After that, reconfigure the site-to-site VPN and see what the results are.
Thanks Richard. The latest service pack and rollup went on at the weekend and it does seemed to have helped. Fingers crossed.
Great And Useful as always short and sweet
thanks richard
Hi Richard,
Thanks for the guide! Works perfectly.
I’ve onlye one problem, i can’t access the TMG server itself over the vpn (all other connections over the tunnel work fine!). Do you’ve any idea where to look?
Maarten
As long as the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall’s internal network interface is included in the scope of the remote network I don’t see why this wouldn’t work. Can you confirm that?
It is, I did a little bit more debugging. Traffic originating form the remote site to the Forefront TMG 2010 server is beeing marked as spoofed. While i can reach any other host behind the Forefront TMG 2010 server (internal network).
i’ve got an access rule to permit traffic originating from the remote site to the local host..
Interesting. TMG is seeing the packet come in from the external interface but the source address is part of the Internal network definition. You won’t be able to add the remote site network to the Internal address definition because that would break your site-to-site connectivity, however. In that case you may not be able to connect to the TMG firewall’s internal IP address from a remote network over site-to-site VPN. You may have to connect to an existing host on the Internal network and connect back to TMG from there, unfortunately.
Hello Richard, I am wondering if you have any suggestions for my problem. I have established working Site to Stie vpn between TMG and Cisco. I am running Forefront TMG 2010 with Service Pack 2 and Update 2
Site to Site VPN is connected and fully functional :
Site A site to site Site B
Client VPn———TMG——–{—isp/internt—-}———VPN(hardware)———-WEB SERVER
From Site A, I can get to the Web server on Site B. However, when client connects through VPN to Site A and try to access Web server or anything on Site B does not work. I have rules same as Internal Network Site A, for VPN Clients to route and access traffic both ways, but still not able to get to web server or Ping. I access the web server with the interlal IP address,which works from Site A but not from Client VPn. Also, I have Client A getting IP from the Site A DHCP pool, so the IP scheme for Site A and VPN Client is same. VPN Client does not have any issues getting to any resources in Site A. Problem is only when Client VPN gets resources on Site B. Any advice?
I don’t believe that client VPN traffic will be able to use the site-to-site VPN tunnel configured on TMG. If your remote access VPN clients need to access resources in site B, you may need to configure a terminal server in site A for them to use.
Hello Richard,
Thanks for the guide – It’s great. I’ve followed and the VPN is working well, the issue is when I try and use RPC over the VPN, TMG drops the connection with:
“A non-SYN packet was dropped because it was sent by a source that does not have an established connection with the ISA Server computer”, and also:
“A connection was abortively closed after one of the peers sent an RST packet.”
I’ve rebuilt the VPN to the tee and there are no firewall or other rules stopping this – Do you know where I might look to troubleshoot this further?
Many thanks, Jesse
Are you having issues connecting to a device on the remote network? Or are you just seeing these events in the log? Non-syn packets being dropped by the firewall is not uncommon but sometimes it is just noise from an application keep-alive and it doesn’t impact general connectivity.
Thanks for the response – I found the issue – It seemed to be strict RPC compliance option in the firewall.
I very much appreciate this guide. It has the very same configuration I needed, TMG att the main office and ASA 5505 at the branch office. I encountered some problems still, firstly, ISAKMP wasn’t activated. I found out that you simply have to “isakmp enable outside” in order to be able to use it in the crypto commands.
Secondly, the VPN just wouldn’t come up, even though configuration was correct done. To get it to work, I simply had to follow your tutorial and do the TMG part again, and that did the trick. The TMG part was the only part I wasn’t unsure about, I guess it is more tricky than the ASA after all.
Thanks a million Richard Hicks!!!
We just acquired a company that has a TMG 2010 system installed and this page is the most concise/complete with regards to support for a IPSEC tunnel. We have not been able to get a tunnel to start between the TMG and our Cisco VPN appliance. The issue appears to be that the TMG does not cope with super-nets. Our network is fully described with a /17, a /18 and a /19. We have tried using ranges that represent those networks, but according to the Cisco logs the TMG is proposing networks that are subsets of those so the Cisco refuses to complete phase 2. One MS article suggests restarting services on the TMG after adding a IPSEC tunnel, but no other guides suggest it. We will test that once we have a maintenance window, but until then I hoped someone might chime in if they have tunnels using anything other than a /24 on each end.
That’s certainly puzzling. It’s been quite a while since I’ve used Forefront TMG 2010 for site-to-site VPN, but I’m sure at some point I configured one with something more than a /24. Let me know if you find out more about this issue though.
Hi, this has been an amazing resource for me, thank you very much. Unfortunately though I am suffering a similar problem to Dan, in that I need my tunnel to be smaller 10.0.2.60/30. I have set it to 10.0.2.60/30 and checked the route rules etc, even the site-to-site summary seems to support my thinking, but my supplier with the Cisco says when the tunnel is initiated from my end, TMG is passing it the whole 10.0.2.0/24 range and it fails on phase 2. Can you shed any light, i’m loosing my mind!
Are you running a fully updated TMG installation? The latest hotfix rollup includes at least one hotfix for site-to-site VPN. If you haven’t done so already, make sure you have SP2 and RU5 installed and see what happens.
Thanks for replying, Richard. Yes, fully up to date (including RU-5)
The problem, as far as I can see it, is that even though I have set a network rule at my end for 10.0.2.60/30 and this is confirmed in the “Site-to-site summary” details that it says I should set at the remote end, my supplier (with the Cisco) tells me my end is trying to initiate the tunnel by specifying a network size of 10.0.2.0/24
I don’t know of a way of confirming at my end if this is the case or not. Or whether this is a known problem, or whether it is actually not possible to start a tunnel with less than a /24 subnet. All examples I ever come across use a .0/24
It’s probably also worth mentioning that thy TMG server is not in the 10.0.2.60/30 range, I don’t know if that makes a difference either.
I just wish there was someway for me to analyse what was actually being send from my end so I could check whether TMG is actually trying to set up the tunnel with the wrong size network.
Interesting. Sounds like TMG might not be working as expected then. The only thing I can suggest is following some of the IPsec VPN troubleshooting found in this article – http://www.isaserver.org/blogs/pouseele/isa-corner/basic-troubleshooting-for-ipsec-based-vpns-53.html. Perhaps you’ll uncover some information there. It does, however, sound like there is a Microsoft support call in your future. 🙂
Hello Richard,
we have a scenario just as described above, but we are having an issue, strange to us. The tunnel wont come up, it only comes up when the site behind the Cisco ASA 525 either initiates an ping, or any simpler.
we are running TMG 2010 v 7.0.9093.644 the remote site is an Cisco ASA 525
Hi Luis,
I believe there was a hotfix released for this, but I can’t seem to find any references to it at the moment. It’s been a long time since I’ve worked with TMG and my memory is fading on things like this. You may want to open a support case with Microsoft, as I’m sure they’d be able to supply it for you. If not, the only thing I can suggest is to continue scouring the Internet for a reference to it. 🙂
You may want to open a support case with Microsoft, as I’m sure they’d be able to supply it for you. If not, the only thing I can suggest is to continue scouring the Internet for a reference to it. 🙂
Hi Richard,
Im doing a practice for a class and I need to create a VPN site to site with IPSEC, If I have two TMG both need to have the same configuration you show us in this post?
If you use the same site-to-site VPN parameters it should work. 🙂