Archive
ISAinfo Forefront TMG 2010 Configuration Reporting Utility
 With the demise of isatools.org a few years ago, many ISA Server and Forefront TMG 2010 administrators have reached out to me to ask where they can find the ISAinfo tool that was previously found on that site. If you’re not familiar with ISAinfo, it was a great utility used for viewing the ISA or TMG configuration by parsing the configuration export. This tool is tremendously useful for providing support, as it includes all of the information required to provide context for troubleshooting. In addition it is an excellent documentation tool.
With the demise of isatools.org a few years ago, many ISA Server and Forefront TMG 2010 administrators have reached out to me to ask where they can find the ISAinfo tool that was previously found on that site. If you’re not familiar with ISAinfo, it was a great utility used for viewing the ISA or TMG configuration by parsing the configuration export. This tool is tremendously useful for providing support, as it includes all of the information required to provide context for troubleshooting. In addition it is an excellent documentation tool.
So, if you’re looking for a reputable location from which to download this tool, look no further. I’ve placed the isainfo.zip file along with the checksums for file verification on my public OneDrive. Enjoy!
ISAinfo.zip – http://1drv.ms/1Q8GOaA
Checksums – http://1drv.ms/1Q8GWqq
Forefront TMG 2010 Computer Certificate Request or Renewal Fails
When attempting to request or renew a computer certificate on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall, you may receive the following error message:
Status: Failed The RPC server is unavailable.

This occurs because the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall does not, by default, allow the protocols and ports required to request or renew a certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA). Common workarounds suggest stopping the firewall completely or creating a rule allowing all protocols and ports from the TMG firewall to the CA. However, both of these workarounds are problematic. Stopping the firewall is a manual process that will cause a service disruption. It also leaves the firewall in an unprotected state. For edge deployment scenarios, the underlying operating system will be exposed directly to untrusted networks, which is a serious security risk. Creating an open access rule is not desirable because it violates the basic security principle of least privilege by allowing more access than is required.
To properly address this issue and allow for the secure request and renewal of certificates without disruption and with the least exposure, it will be necessary to create an access rule on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall to allow all dynamic ports (TCP 49152-65535) from the local host network to the IP address of the CA for all users.
Note: Allowing all dynamic ports (TCP 49152-65535) might also be considered too much access from the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall to the CA. It is possible to restrict the dynamic ports used by TMG and further tighten the access rule, if required. For information about restricting dynamic ports, click here.
In addition to the access rule allowing all dynamic ports, it will also be necessary to make a change to a system policy rule. To do this, right-click the Firewall Policy node in the navigation tree and choose All Tasks, System Policy, and then Edit System Policy. In the Authentication Services group highlight Active Directory and clear the checkbox next to Enforce strict RPC compliance.

Once these changes have been made you can now request or renew a computer certificate on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall successfully.

Windows Azure Multifactor Authentication and Forefront TMG 2010
When Microsoft first announced Windows Azure Multi-Factor Authentication, a cloud-based strong authentication solution, my first thought was “I wonder if it works with Forefront TMG 2010?” Being cloud-based, my first thought was perhaps not. However, once I started digging in to it I quickly learned that it includes a software component that can be installed on-premises and will even integrate with on-premises security solutions via a number of interfaces, including RADIUS. Forefront TMG 2010 has supported RADIUS authentication for many years, so I put together a test lab and in no time at all I had Windows Azure multi-factor authentication working with Forefront TMG 2010 remote access VPN. Forefront TMG 2010 integrated with Windows Azure multi-factor authentication provides the highest level of protection for remote access users. Leveraging Windows Azure cloud-based strong authentication is extremely cost effective, with very low per user or per authentication costs and no on-premises hardware to purchase. The Windows Azure public cloud, which is ISO/IEC27001:2005 certified, provides the most secure and reliable strong authentication service available today. To learn how to configure Forefront TMG 2010 to work with Windows Azure multi-factor authentication, click here.
Forefront TMG 2010 Protocols and Ports Reference
When deploying Forefront TMG 2010 as a forward or reverse proxy, many organizations will place their TMG firewalls in a perimeter or DMZ network to provide an additional layer of protection for their proxies. When deployed in this manner, configuring perimeter firewalls to allow proper communication to and from the Forefront TMG firewall can be challenging. Although the Service Overview and Network Port Requirements for Windows document on TechNet includes information about ISA server (which also applies to TMG) it includes all protocols and ports used by TMG in all deployment scenarios. This can be confusing when you simply want to allow TMG firewalls in a perimeter network to communicate with an Enterprise Management Server (EMS) on the internal network, or simply manage a TMG firewall in a perimeter network from a management workstation on the internal network. Opening all of the ports listed in the Microsoft KB article mentioned above would be unnecessary and would violate the principle of least privilege, which dictates that only the specific ports required for communication should be opened.
Note: This reference covers typical TMG configurations and may not include all protocols and ports required for every deployment scenario. For example, if you are using RADIUS or RSA for authentication, have configured connectivity verifiers or a remote SQL server, or have deployed Forefront TMG 2010 for Exchange integration, each of these configurations will require additional perimeter firewall access. Also, don’t forget that your perimeter firewalls will need to allow access to the protocols and ports required for the services you are accessing/publishing through Forefront TMG 2010.
For reference, here are the protocols and ports required for specific, common Forefront TMG 2010 deployment scenarios:
EMS to TMG
TCP 135, 10000-65535* – RPC
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
TMG to EMS
TCP 445 – CIFS
UDP 445 – CIFS
TCP 2171 – MS Firewall Storage (domain-joined only)
TCP 2172 – MS Firewall Storage Secure (workgroup mode only)
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
TMG to DCs
Domain joined…
TCP 88 – Kerberos
UDP 88 – Kerberos (send receive)
UDP 123 – NTP
TCP 135, 49152-65535* – RPC
TCP 389 – LDAP
UDP 389 – LDAP
TCP 445 – CIFS
UDP 445 – CIFS
TCP 3268 – LDAP Global Catalog
Non domain-joined…
TCP 389 – LDAP (required only for pre-authentication in reverse proxy scenarios)
TCP 636 – LDAPS (required only for pre-authentication in reverse proxy scenarios)
TMG to DNS
TCP 53 – DNS (send receive)
UDP 53 – DNS
Primary EMS to Replica EMS
TCP 135, 49152-65535* – RPC
TCP 2173 – MS Firewall Storage Replication
Replica EMS to Primary EMS
TCP 135, 49152-65535* – RPC
TCP 445 – CIFS
UDP 445 – CIFS
TCP 2171 – MS Firewall Storage – domain-joined only
TCP 2172 – MS Firewall Storage (Secure) – workgroup mode only
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
Web Proxy Client to TMG
TCP 80 – HTTP (WPAD only)
TCP 8080 – HTTP Proxy
Firewall Client to TMG
TCP 80 – HTTP (WPAD only)
TCP 1745 – Firewall Client Control Channel
UDP 1745 – Firewall Client Control Channel
TCP 1024-65535 – All high ports**
UDP 1024-65535 – All high ports**
Management Workstation to TMG
TCP 135, 10000-65535* – RPC
TCP 2171 – MS Firewall Storage – Domain mode only
TCP 2172 – MS Firewall Storage (Secure) – Workgroup mode only
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
*The default dynamic port range for Windows Server 2008 R2 is 49152-65535. When TMG is installed this setting is changed to 10000-65535. This does not apply to TMG EMS, however. RPC can be configured to use a smaller range of dynamic ports, if necessary. For more information, please see Microsoft KB 154956.
**The Forefront TMG 2010 Firewall Client is designed to operate without a firewall between itself and the TMG firewall. It is highly recommended that you avoid this design whenever possible. If this is unavoidable, all TCP and UDP high ports will have to be opened, as the TMG Firewall Client control channel utilizes random high ports and cannot be restricted as RPC can.
Forefront TMG 2010 Turns Two Years Old
Today marks the second anniversary of the release to manufacturing (RTM) for Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010. In the two years since its release Microsoft has provided two major service packs that have increased stability, improved performance and scalability, and also added some helpful new functionality. During this time the product also achieved Common Criteria (level EAL4+) certification. As we approach the end of mainstream support for Microsoft ISA Server 2006 SP1, now is a good time to begin evaluating Forefront TMG 2010 and to start planning your migration!
ISA Server 2006 Hotfix Rollup – September 2011
A hotfix rollup for Microsoft ISA Server 2006 is now available. The hotfix rollup resolves several reported issues with ISA Server, including:
KB2618727 – Users in remote forests cannot change their passwords through ISA Server 2006.
KB2620088 – Large files become corrupted during file transfer through the Socks v4 client.
KB2620076 – Outlook Web App clients are not timed out after the ISA FBA idle time-out is reached.
KB2620069 – ISA 2006 may crash with the error “DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL (d1)”.
KB2622172 – ISA 2006 blocks published website requests for URLs that include carriage returns (CR) or linefeeds (LF).
The latest ISA server 2006 hotfix rollup can be downloaded here. After applying this update, the new ISA Server 2006 build number will be 5.0.5723.526.
Microsoft ISA Server 2004/2006 Migration to Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG)
Jim Harrison and Mohit Saxena discuss Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) migration strategies with David Tesar in this video on TechNet Edge.
MSDE Performance with Microsoft ISA Server 2006
I realize that MSDE performance is an oxymoron, but the performance of the MSDE database included with Microsoft ISA Server 2006 is essential to the operation of the ISA firewall. By default, if ISA is unable to write log data to the database, the firewall will enter lockdown mode and stop servicing requests. To ensure the availability of the ISA firewall, it is important to understand the limitations that are inherent with MSDE, and also the steps to take to improve performance when logging to an MSDE database.
There are several logging options to choose from when installing ISA. Selecting the ‘advanced logging’ feature will install the Microsoft SQL Server 2000 Desktop Engine (MSDE) database to support logging.
The advanced logging option using MSDE requires more resources than text file logging (in terms of processor utilization, memory consumption and disk I/O), but unlike text file logging there is the added benefit of viewing historical log data in the ISA management console.
To be honest, I have never been a fan of using MSDE with ISA. In terms of performance, it is not very robust. MSDE was designed originally as an alternative to the Jet database engine included with Microsoft Access and was never intended to be used for enterprise applications. MSDE is based on SQL Server 2000, which by my math is over nine years old as of this writing. That is an eternity in technology time. Also, MSDE on ISA limits the database size to 1.5GB, and by design includes a workload governor that can impede performance in busy environments. Personally, I prefer text logging because it is much more robust, scalable, and higher performing, especially in very busy enterprise deployments. For me, the need to view historical data in the ISA management console is not critical, as I am comfortable with looking through text log files using the command line. I make liberal use of utilities such as findstr.exe and tail.exe (the latter of which is included in the Windows Server 2003 Resource Kit tools), as well as the Microsoft Log Parser. That’s just me though. : )
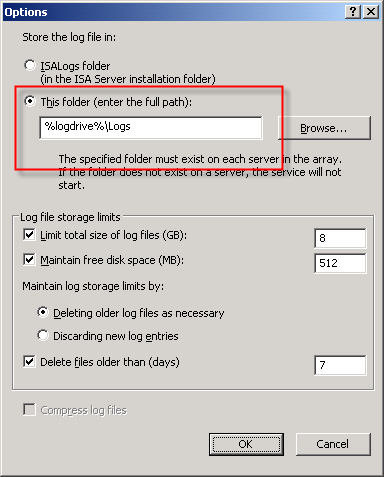
Of course there are many small and mid-sized deployments for which MSDE is perfectly suited and quite capable of performing adequately. In those scenarios, it is important that we follow some implementation best practices and perform additional maintenance to ensure optimum performance when using MSDE. First and foremost, the MSDE database files should be placed on a separate partition from the system partition. This will reduce disk contention and file fragmentation. By default, the log files are contained in the \Program Files\Microsoft ISA Server\ISALogs folder on the system partition.
You can change the location of the database files by opening the ISA management console, highlighting ‘Monitoring’, then selecting the option to ‘Configure Firewall Logging’ or ‘Configure Web Proxy Logging’.
Next, click the ‘Options…’ button next to the ‘MSDE Database’ option, then select the radio button next to ‘This folder (enter full path):’ and specify a location to store the log files. If you are making this change on an ISA Enterprise array, this location must exist on ALL array members. You have the option to use a system variable here, such as %logdrive%, which can simplify configuration for enterprise deployments.
Although less critical when you have a separate partition for the log files, disk fragmentation can reduce MSDE performance as well. You can use the native Windows disk defragmentation tool (defrag.exe) to defragment the partition, or if you prefer only to defragment the database files themselves you can use contig.exe from Sysinternals.
Note: This screen shot is from a little used test machine, so the level of fragmentation is minimal. On a busy system that has been in production for years, there will almost certainly be more fragmentation than you see here.
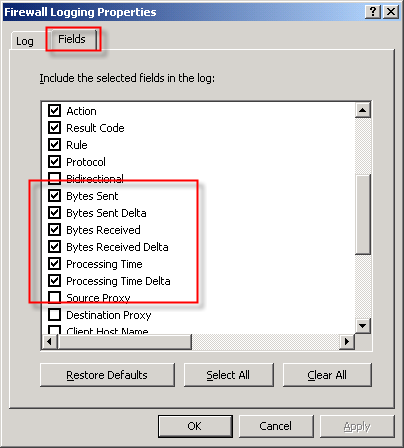
In addition to the best practices outlined above, another way to improve MSDE performance is to reduce the amount of data logged in the first place. This can be accomplished in several ways. To begin, review the log fields that are selected by default. You can find the log fields on the Firewall or Web Proxy logging properties window and clicking on the ‘Fields‘ tab. If there are fields that contain information that aren’t required, deselect them. Some fields that are enabled by default and are commonly omitted are the bytes sent and received (and delta) fields and processing time (and delta) fields. Review all of the log fields to determine the minimum data required.
You might also consider not logging traffic processed by the default deny rule. While this can significantly reduce the amount of data logged in busy environments, it does reduce visibility in to what types of traffic the ISA firewall is rejecting. A better alternative is to create specific access rules for uninteresting traffic (e.g. DHCP requests, NetBIOS name resolution broadcasts, etc.) and configure the rule not to log requests that match.
You can also disable the option to log traffic blocked by flood mitigation settings. Flood mitigation settings can be found in the ISA management console by expanding the ‘Configuration’ node, highlighting the ‘General’ node, then click on the ‘Configure Flood Mitigation Settings’ link.
Considering the many limitations imposed by MSDE, you might think that using a remote SQL server is the answer to all of these problems. Having a dedicated system running the latest version of SQL would certainly better than MSDE. However, network connectivity issues and throughput can potentially impede performance using this option. Thankfully Forefront Threat Management Gateway 2010 includes some significant enhancements to logging that address these issues. First, the native database logging option now uses SQL 2008 Express, which is a big improvement over MSDE. Also, TMG database logging now includes an option to queue logged data locally if for any reason the database is unreachable. The log queuing feature of TMG now makes remote SQL logging a viable and compelling option for logging in the future.
For additional information about remote SQL logging, see my previous posts Remote SQL Logging with Microsoft ISA Server 2006 and A Few Notes Regarding Remote SQL Logging with Microsoft ISA Server and Forefront Threat Management Gateway.
For more detail about how logging works in ISA, and for additional information on the various logging options available, please refer to the Monitoring, Logging, and Reporting Features in ISA Server 2006 document on TechNet.
ISA 2006 Flood Mitigation Strategies
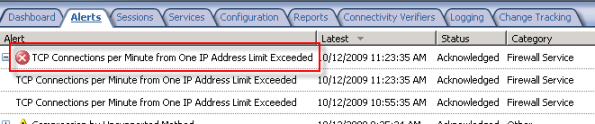
The flood mitigation features included in Microsoft ISA Server 2006 were one of many improvements over previous versions of ISA. Enabled by default, this enhanced network protection functionality allows the ISA firewall to withstand direct attacks (e.g. DoS or SYN flood) and provides resiliency in the event of a worm breakout. There are times, however, when this feature can impede valid network communication. If, for example, a host protected by the ISA firewall is very busy it may run in to connection limits imposed by the firewall. When this happens you may see the following error in the event log: ‘TCP connections per minute from one IP address limit exceeded’.
When legitimate network communication is dropped for this reason, it is possible to configure the firewall to allow more connections for this host. This is accomplished by opening the ISA management console, expanding the ‘Configuration’ node in the console tree, then clicking on the ‘Configure Flood Mitigation Settings’ link in the ‘Additional Security Policy’ section.
Too often I see administrators disable flood mitigation altogether. This is strongly discouraged. I also see administrators raise connection limits for ALL hosts by clicking on the ‘Edit…’ button and entering a new limit. This is also a bad practice. The best way to resolve this problem is to add the host(s) to a computer set, then add that computer set to the ‘IP Exceptions’ list.
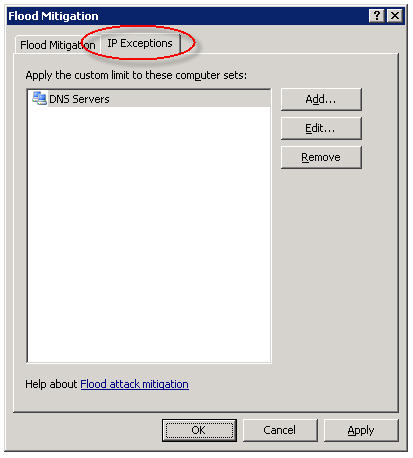
In my experience this often needs to be done for DNS servers and for busy mail servers. Your alerts will tell you which systems are good candidates for the exception list though, so be sure to monitor your ISA firewalls closely.