Enable Hybrid Cloud with Forefront TMG 2010 and Windows Azure
Earlier this year I published an article on ISAserver.org on how to enable cross-premises network connectivity to Windows Azure using Forefront TMG 2010. When I wrote that piece, Windows Azure virtual networking was still in preview (beta). Since that time, Windows Azure virtual networking has been officially released, with some significant changes in features, functionality, and configuration steps. Many people noticed that their existing Forefront TMG 2010 to Windows Azure site-to-site VPN stopped working at this time and assumed that support for TMG had been dropped. Not so! Forefront TMG 2010 site-to-site VPN does work with Windows Azure virtual networks, and is indeed supported as it meets the minimum requirements for VPN devices connecting to Windows Azure virtual networks outlined here.
Configuring site-to-site VPN connectivity between the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall and Windows Azure virtual networks is not without a minor drawback, however. One of the new features of Windows Azure virtual networking is point-to-site VPN using SSTP. Unfortunately this feature requires that you configure dynamic routing on your Windows Azure virtual network, and dynamic routing makes use of IKEv2, which the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall does not support. So, if you want to enable cross-premises network connectivity to Windows Azure using Forefront TMG 2010, you will not be able to take advantage of this new point-to-site VPN connectivity option.
Important Note: Windows Azure virtual networking site-to-site VPN requires that your VPN endpoint have a public IPv4 address assigned to it’s external network interface. If your Forefront TMG 2010 firewall is located behind a border router or edge firewall performing NAT, site-to-site VPN connectivity with Windows Azure will not be possible.
To configure cross-premises network connectivity with Windows Azure, log in to the Windows Azure portal and select Networks in the navigation pane, then click on Create Virtual Network. Enter a Name for the virtual network, specify a Region, and provide an Affinity Group Name and select the appropriate Subscription.
Enter the names and IP addresses of any DNS servers to be used by machines in this virtual network and select the option to Configure site-to-site VPN. Do NOT select the option to Configure point-to-site VPN.
Provide a name for the site-to-site connection and enter the IP address assigned to the external network interface of the Forefront TMG firewall. In addition, specify the network address space in use on the private, on-premises side of the connection.
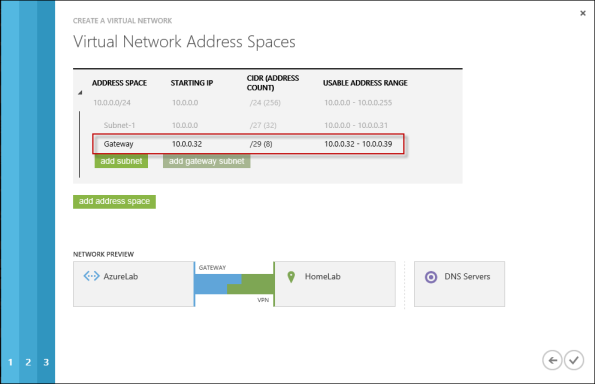
Define your virtual network subnet as required. Here I’ve chosen to use the 10.0.0.0/24 address space. Define any additional subnets as necessary and then click Add gateway subnet.
Click on the newly created virtual network and then click on Dashboard. Click Create Gateway and choose Static Routing.
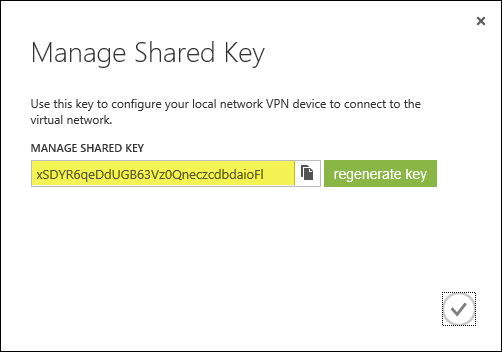
Once the gateway has been created, make a note of the Gateway IP Address and then click Manage Key. Copy this key as it will be required when configuring the site-to-site VPN on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall.
On the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall, open the management console and select Remote Access Policy (VPN). Click the Remote Sites tab in the center pane and then click Create VPN Site-to-Site Connection in the Tasks pane. When the Create Site-to-Site Connection Wizard begins, enter a name for the new site-to-site network.
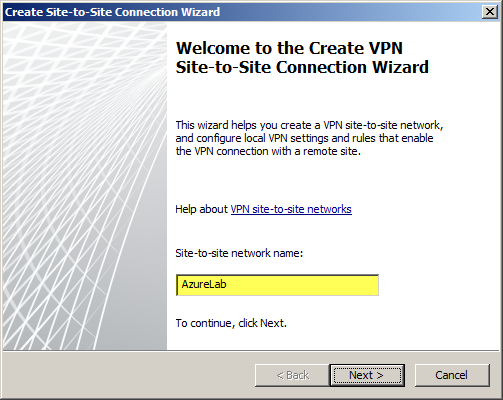
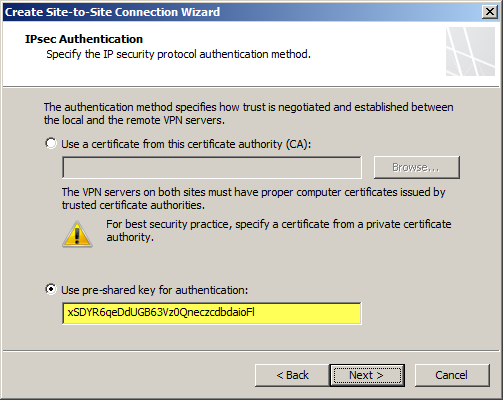
Select IP Security protocol (IPsec) tunnel mode.

Enter the IP address of the Windows Azure virtual network gateway and the local VPN gateway IP address, which is the IP address assigned to the external network interface of the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall.

Copy the pre-shared key from the Windows Azure virtual network gateway.
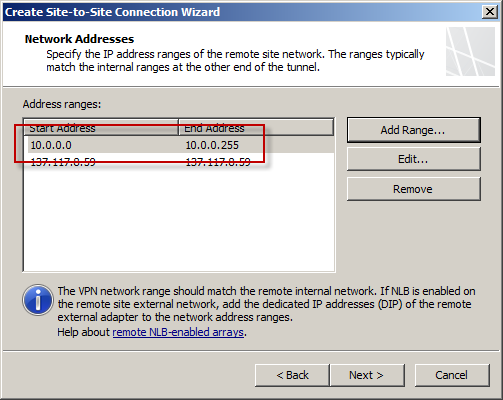
The IP address of the Windows Azure virtual network gateway will be automatically added to the network address list. Click Add Range and add the IP address range you defined earlier for the virtual network.
Select the option Create a network rule specifying a route relationship.

Any communication between the on-premises network and the Windows Azure virtual network must be allowed by firewall policy. You can create an access rule now, or create one later.
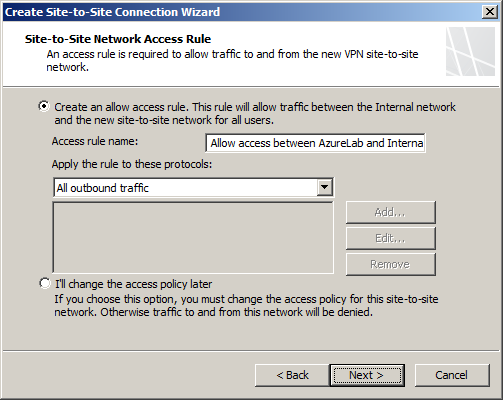
Review the configuration settings and click Finish.

Before applying the configuration, right-click the site-to-site connection and choose Properties, select the Connection tab, and then click IPsec Settings.
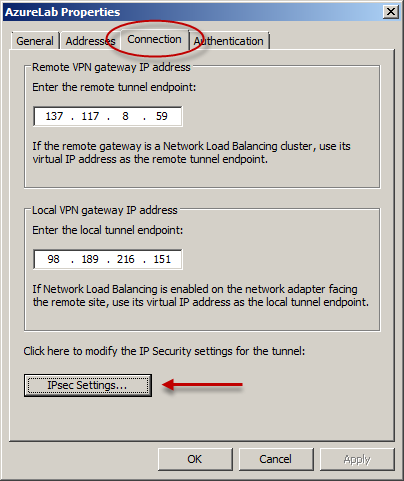
On the Phase I tab select SHA1 for the Integrity algorithm and leave the remaining settings at their defaults.

On the Phase II tab select SHA1 for the Integrity Algorithm. Select the option to Generate a new key every 102400000 Kbytes and clear the option to Use Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS).
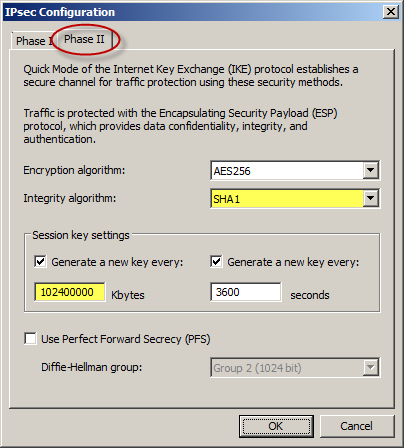
Once complete, apply the configuration. Finally, set the Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall’s external interface to 1350 bytes by opening an elevated command prompt and issuing the following command:
netsh interface ipv4 set interface <interface_name_or_index> mtu=1350
For example:
netsh interface ipv4 set interface external mtu=1350
The Windows Azure management console should now indicate that you have successfully established a site-to-site VPN to the remote virtual network.
When you configure a new Windows Azure virtual machine, you can specify that the machine be placed in to your virtual network.
The new virtual machine should now be reachable from your on-premises network using the site-to-site VPN configured on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall.













Thanks for the instructions. I followed it exactly and everything works fine except one thing. I can do HTTPS, RDP, open shared folders from the internal network to an Azure VM, but HTTP will not work. After one minute I get a time out. From the Azure VM I can HTTP/HTTPS, RDP, open shared folders on the internal network. I even joined the Azure VM to our domain. Seems that all traffic flows in both directions fine except HTTP from internal network (including TMG server) to Azure VMs.
Any ideas?
That certainly is an odd issue. Perhaps it is a firewall issue on the Azure VM? I’d suggest breaking out the protocol analyzer and observing the traffic from both sides to see what is up. Very puzzling though!
Hi Richard, Do you know if something has changed since the date you wrote this guide? I’m following the steps you described and cannot connect the VPN tunnel.
Thanks!!
No, I think everything is still the same…