Archive
Forefront TMG 2010 Protocols and Ports Reference
When deploying Forefront TMG 2010 as a forward or reverse proxy, many organizations will place their TMG firewalls in a perimeter or DMZ network to provide an additional layer of protection for their proxies. When deployed in this manner, configuring perimeter firewalls to allow proper communication to and from the Forefront TMG firewall can be challenging. Although the Service Overview and Network Port Requirements for Windows document on TechNet includes information about ISA server (which also applies to TMG) it includes all protocols and ports used by TMG in all deployment scenarios. This can be confusing when you simply want to allow TMG firewalls in a perimeter network to communicate with an Enterprise Management Server (EMS) on the internal network, or simply manage a TMG firewall in a perimeter network from a management workstation on the internal network. Opening all of the ports listed in the Microsoft KB article mentioned above would be unnecessary and would violate the principle of least privilege, which dictates that only the specific ports required for communication should be opened.
Note: This reference covers typical TMG configurations and may not include all protocols and ports required for every deployment scenario. For example, if you are using RADIUS or RSA for authentication, have configured connectivity verifiers or a remote SQL server, or have deployed Forefront TMG 2010 for Exchange integration, each of these configurations will require additional perimeter firewall access. Also, don’t forget that your perimeter firewalls will need to allow access to the protocols and ports required for the services you are accessing/publishing through Forefront TMG 2010.
For reference, here are the protocols and ports required for specific, common Forefront TMG 2010 deployment scenarios:
EMS to TMG
TCP 135, 10000-65535* – RPC
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
TMG to EMS
TCP 445 – CIFS
UDP 445 – CIFS
TCP 2171 – MS Firewall Storage (domain-joined only)
TCP 2172 – MS Firewall Storage Secure (workgroup mode only)
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
TMG to DCs
Domain joined…
TCP 88 – Kerberos
UDP 88 – Kerberos (send receive)
UDP 123 – NTP
TCP 135, 49152-65535* – RPC
TCP 389 – LDAP
UDP 389 – LDAP
TCP 445 – CIFS
UDP 445 – CIFS
TCP 3268 – LDAP Global Catalog
Non domain-joined…
TCP 389 – LDAP (required only for pre-authentication in reverse proxy scenarios)
TCP 636 – LDAPS (required only for pre-authentication in reverse proxy scenarios)
TMG to DNS
TCP 53 – DNS (send receive)
UDP 53 – DNS
Primary EMS to Replica EMS
TCP 135, 49152-65535* – RPC
TCP 2173 – MS Firewall Storage Replication
Replica EMS to Primary EMS
TCP 135, 49152-65535* – RPC
TCP 445 – CIFS
UDP 445 – CIFS
TCP 2171 – MS Firewall Storage – domain-joined only
TCP 2172 – MS Firewall Storage (Secure) – workgroup mode only
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
Web Proxy Client to TMG
TCP 80 – HTTP (WPAD only)
TCP 8080 – HTTP Proxy
Firewall Client to TMG
TCP 80 – HTTP (WPAD only)
TCP 1745 – Firewall Client Control Channel
UDP 1745 – Firewall Client Control Channel
TCP 1024-65535 – All high ports**
UDP 1024-65535 – All high ports**
Management Workstation to TMG
TCP 135, 10000-65535* – RPC
TCP 2171 – MS Firewall Storage – Domain mode only
TCP 2172 – MS Firewall Storage (Secure) – Workgroup mode only
TCP 3847 – MS Firewall Control
*The default dynamic port range for Windows Server 2008 R2 is 49152-65535. When TMG is installed this setting is changed to 10000-65535. This does not apply to TMG EMS, however. RPC can be configured to use a smaller range of dynamic ports, if necessary. For more information, please see Microsoft KB 154956.
**The Forefront TMG 2010 Firewall Client is designed to operate without a firewall between itself and the TMG firewall. It is highly recommended that you avoid this design whenever possible. If this is unavoidable, all TCP and UDP high ports will have to be opened, as the TMG Firewall Client control channel utilizes random high ports and cannot be restricted as RPC can.
Configuring Splunk Universal Forwarder on Forefront TMG 2010
Aggregating logged data from security devices such as the Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 firewall is a top priority for many security engineers. Forefront TMG and its predecessor, ISA Server, have always lacked an integrated facility to forward logged data to an external event management system. Often the administrator will have to devise an elaborate process that consists of batch files or scripts that collect firewall and web proxy logs and copy them to another location where they can be consumed. In the past I’ve demonstrated how third-party utilities can convert firewall log data to the syslog format as well.
Splunk is one of the more popular log management systems in use today, and to make it easier to get Forefront TMG log data in to Splunk we can use the Splunk Universal Forwarder. The Universal Forwarder is a utility that installs on the Forefront TMG firewall and monitors the folder containing W3C formatted text log files. The Universal Forwarder has a small footprint and consumes few resources, making it the ideal method to collect Forefront TMG log data and deliver it to the Splunk indexing server for analysis and archiving. The Splunk Universal Forwarder can be downloaded here.
Configuring Forefront TMG 2010
Before installing the Universal Forwarder, the Forefront TMG firewall must be configured to log to text file format. To change the log file format, open the Forefront TMG management console and highlight the Logs & Reports node in the navigation tree, select the Logging tab in the center console window, and then click Configure Firewall Logging in the Tasks pane on the right.

Select the option to log to File and choose the W3C extended log file format from the drop down box below. Repeat these steps to configure web proxy logging.

When the option to log to text file format is chosen, native Forefront TMG reports cannot be generated and access to historical log data in the Forefront TMG management console is no longer possible. Clicking Ok will generate the following warning message:
Reports cannot be generated with the currently selected logging method. To generate reports, use logging to SQL Server Express databases (on the local server).

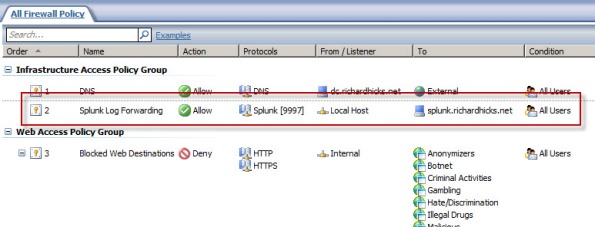
An access rule must be created to allow the Splunk Universal Forwarder to communicate with the Splunk indexing server. The source will be the local host network, the destination will be the Splunk indexing server, and the protocol will be TCP 9997 (outbound), which is the default port used by the Splunk Universal Forwarder.
Configuring Splunk Universal Forwarder
Next, install the Splunk Universal Forwarder on the Forefront TMG firewall. When prompted, enter the hostname, FQDN, or IP address of your indexing server and specify a TCP port to use (the default is TCP port 9997).

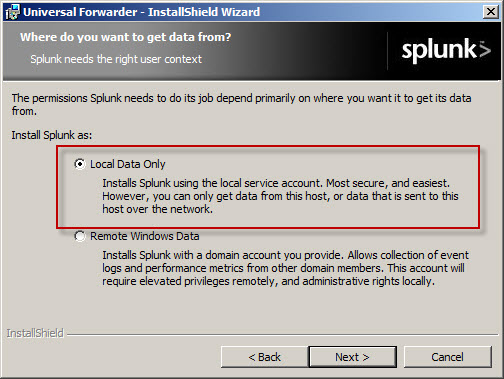
Select the option to forward Local Data Only.
The Forefront TMG firewall will create new text log files each day and store them in the specified log files folder. Specify a Path to monitor by clicking Directory… and selecting C:\Program Files\Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway\Logs (or the path where your log files are stored, if different from the default).

Configure Splunk Indexing Server
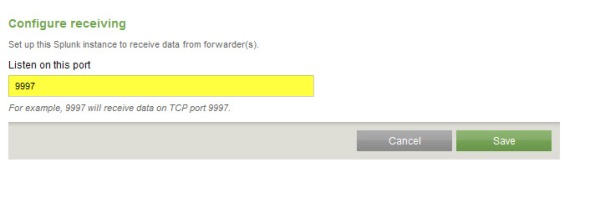
Once the installation is complete, open the Splunk Manager and click Forwarding and receiving.

Click the Add new link next to Configure receiving.
Configure the indexing server to Listen on this port and enter 9997.
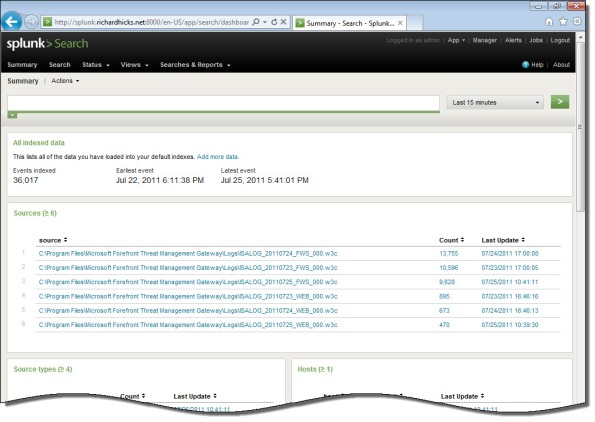
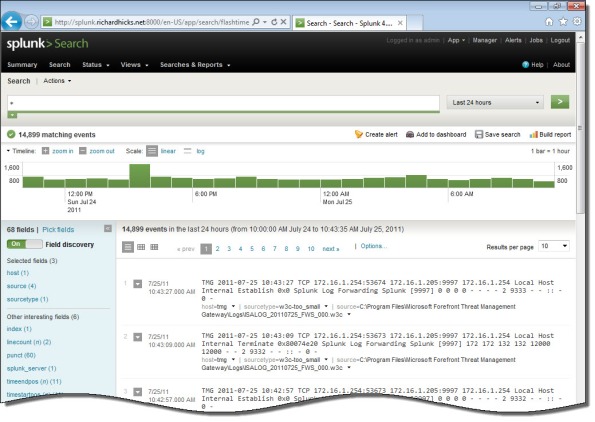
Once you’ve configured Splunk to receive data from the forwarder, Forefront TMG firewall and web proxy log data should appear on the indexing server.
Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF) Reliability Workbooks
The Microsoft Operations Framework (MOF) provides important guidance for IT professionals responsible for maintaining and operating various Microsoft technologies. The MOF Technology Library includes a series of workbooks that provide detailed knowledge, tasks, and schedules required to keep these technologies operating efficiently and without issue. There are workbooks available today for many Microsoft infrastructure and application services, including Active Directory, DNS, Exchange, SQL, IIS, and many more. Reliability workbooks for Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG) and DirectAccess were recently added to the library. The Network Load Balancing (NLB) workbook will also be helpful for many TMG and UAG administrators. If you are responsible for deploying or managing these technologies in your organization, these workbooks are sure to be beneficial.