Archive
Bug in Forefront TMG 2010 Service Pack 2
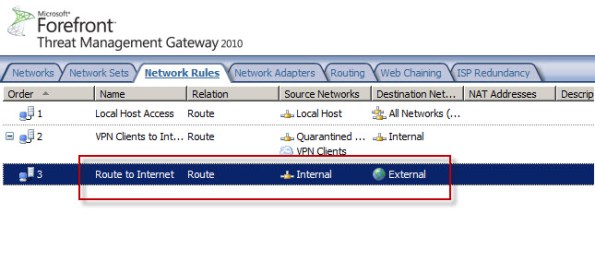
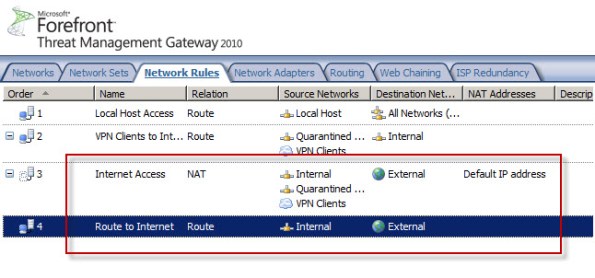
Today I confirmed a bug in Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Forefront TMG 2010 that was discovered by Jason Jones. If you have deleted the default Internet Access network rule and replaced it with something else, installing SP2 for Forefront TMG 2010 mysteriously restores this rule. Unfortunately it places the default Internet Access rule ahead of your custom rule which in most cases will cause serious problems. This bug only affects Forefront TMG 2010 configurations where the default Internet Access network rule has been specifically deleted. If you’ve altered this rule in any way, those changes are unaffected.
Before Forefront TMG SP2 installation…
After Forefront TMG SP2 installation…
Microsoft Security Bulletin MS11-083 and Forefront TMG 2010
Included in the November Microsoft security bulletin release was security update MS11-083 (KB2588516) that addresses a critical vulnerability in TCP/IP that could allow remote code execution. Forefront TMG 2010 firewalls are protected from this vulnerability, as the firewall engine’s kernel mode driver processes packets even before the operating system sees them. More information about how the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall engine and service work can be found here [this document is for ISA, but TMG is similar]. Although the underlying operating system’s TCP/IP networking stack is protected by the Forefront TMG firewall engine driver, TMG administrators are still strongly encouraged to install the MS11-083 update as soon as possible.
Error 0x8004FE2F Activating Windows on Forefront TMG 2010 Protected Network
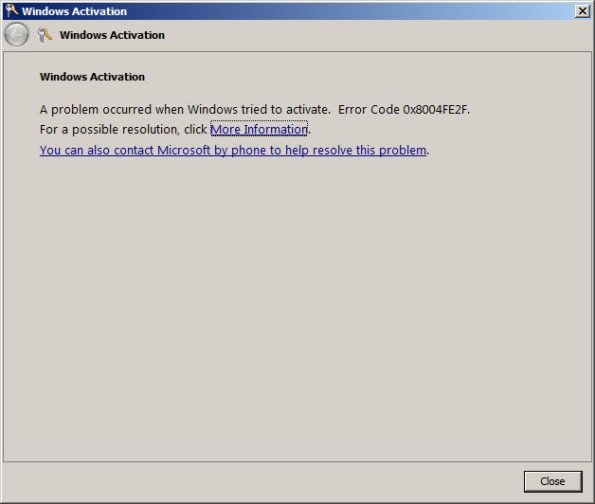
When attempting to activate Windows Server 2008R2 you may receive one of the following error messages:
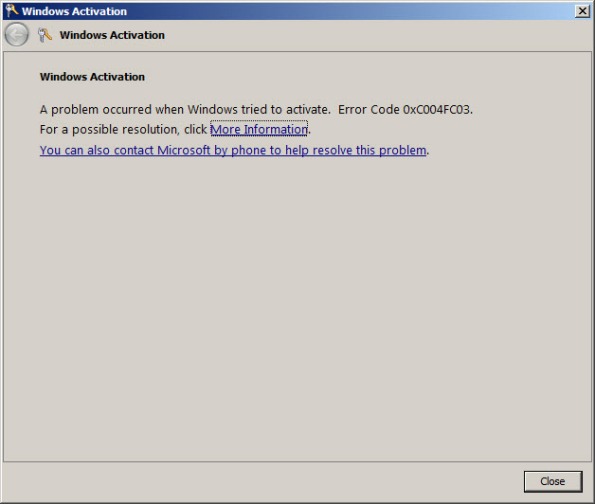
A problem occurred when Windows tried to activate. Error Code 0x8004FE2F
Or…
A problem occurred when Windows tried to activate. Error Code 0xC004FC03
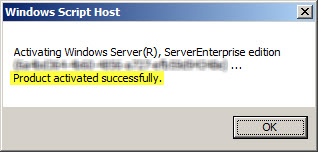
If you attempt to activate Windows from the command line using slmgr.vbs -ato you may also encounter one of the following error messages:
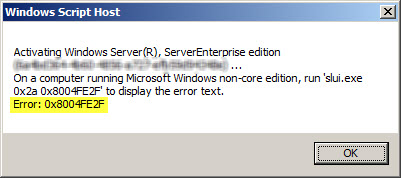
Activating Window Server(R), ServerEnterprise edition {GUID}...
On a computer running Microsoft Windows non-core edition, run 'slui.exe
0x2a 0x8004FE2F' to display the error text.
Error: 0x8004FE2F
Or…
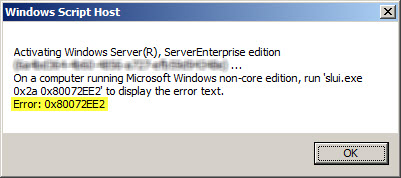
Activating Window Server(R), ServerEnterprise edition {GUID}...
On a computer running Microsoft Windows non-core edition, run 'slui.exe
0x2a 0x80072EE2' to display the error text.
Error: 0x80072EE2
The problem may occur for systems that are located on a network that is protected by a Forefront TMG 2010 firewall, and the access rule that allows the traffic requires authentication. The Windows activation process relies on WinHTTP and by default, WinHTTP communication is sent as SecureNAT client traffic. SecureNAT clients unfortunately cannot be authenticated, so the request fails.
There are two ways resolve this issue. The first is to configure WinHTTP on the Windows system you are trying to activate to use a proxy serverexplicitly. Open an elevated command prompt and enter the following command:
netsh winhttp set proxy <name or IP address of proxy server>:<port>
For example:
netsh winhttp set proxy tmg.richardhicks.net:8080
Instead of making this change to each system you want to activate, an alternative is to create an anonymous access rule on the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall that allows HTTP and HTTPS traffic to those destinations required to activate Windows. Using the Forefront TMG 2010 management console, create an access rule that allows HTTP and HTTPS from the Internal network to a Domain Name Set that contains the following destinations for all users:
activation.sls.microsoft.com.nsatc.net go.microsoft.com *.sls.microsoft.com
Make sure this rule is placed before any other rules for HTTP or HTTPS that require authentication.
Once configured, activating Windows should work without issue.
Configuring Forefront TMG 2010 HTTPS Inspection Inclusion List
When HTTPS inspection is configured and enabled on a Forefront TMG 2010 firewall, the administrator has the option to define web sites to exclude from HTTPS inspection. This may be required for a variety of reasons. For example, an administrator may need to exclude certain destinations to address privacy concerns, or perhaps HTTPS inspection breaks an application that uses SSL to tunnel non-HTTP protocols. All HTTPS web sites are inspected except for those sites defined as Destination Exceptions.

Beginning with Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Forefront TMG 2010, administrators can now define an explicit inclusion list for HTTPS inspection. Sites included on this list will be subject to HTTPS inspection, while all other destinations will be excluded. To define an HTTPS inspection inclusion list, create a Domain Name Set and populate it with those destinations for which you explicitly want to enforce HTTPS inspection.

After saving and applying the configuration, copy this VBScript file to the TMG firewall, then open an elevated command prompt and type the following command:
cscript.exe ConfigureHTTPSiInclusionList.vbs <DomainNameSetName>
Substitute <DomainNameSetName> in the command above with the name of the Domain Name Set created earlier. Once configured, the Destination Exceptions tab of the HTTPS Outbound Inspection properties will be greyed out, and only those sites included in the Domain Name Set defined as the HTTPS inspection inclusion list will be subject to HTTPS inspection. All other destinations will be excluded. You can still define Source Exceptions as needed, however.

Only one Domain Name Set can be specified as the HTTPS inspection inclusion list. Running the command without parameters removes any configured inclusion list and returns HTTPS inspection back to its original state.
For more information regarding HTTPS inspection inclusion lists, refer to KB2619986.
Slipstream Service Pack 2 for Forefront TMG 2010
Now that Service Pack 2 (SP2) for Microsoft Forefront TMG 2010 is available I’ve had numerous people ask me about the process of slipstreaming the service pack with the Forefront TMG 2010 installation media. Having Forefront TMG 2010 with SP2 slipstreamed is a great time saver if you install TMG frequently like I do, but it is also essential if you wish to install Forefront TMG 2010 on a read-only domain controller (RODC). Last year when service pack 1 for Forefront TMG 2010 was released I wrote this post on how to slipstream the service pack. The process is nearly identical with Forefront TMG 2010 SP2 with the exception that there are a few more steps required because of TMG SP2’s dependencies on SP1 and software update 1 for TMG SP1.
To slipstream SP2 with the Forefront TMG 2010 installation media, begin by copying the contents of your Forefront TMG 2010 DVD or extracting the ISO to a temporary folder. Next, download Forefront TMG 2010 SP1, Forefront TMG 2010 SP1 software update 1, and Forefront TMG 2010 SP2. Software update 1 for Forefront TMG 2010 SP1 and SP2 for Forefront TMG 2010 are both .exe files that can’t be used for slipstreaming. To support slipstreaming we’ll need to extract the .msp files from them by opening an elevated command prompt and issuing the following commands:
For software update 1 for Forefront TMG 2010 SP1
TMG-KB2288910-amd64-ENU.exe /t d:\temp\SP1U1
For Forefront TMG 2010 SP2
TMG-KB2555840-amd64-ENU.exe /t d:\temp\SP2
Now begin the slipstreaming process by navigating to the \FPC folder of the TMG installation source and then issuing the following commands:
First, slipstream SP1 for Forefront TMG 2010
msiexec /a MS_FPC_Server.msi /p d:\temp\sp1\TMG-KB981324-AMD64-ENU.msp
Next, slipstream software update 1 for Forefront TMG 2010 SP1
msiexec /a MS_FPC_Server.msi /p d:\temp\sp1u1\TMG-KB2288910-amd64-ENU.msp
Finally, slipstream Forefront TMG 2010 SP2
msiexec /a MS_FPC_Server.msi /p d:\temp\sp2\TMG-KB2555840-amd64-ENU.msp
Once complete, use your favorite tool to burn a DVD or create an ISO file.
Important Note: If you install the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client from the new SP2 slipstreamed installation source, you will still need to install the October 2011 Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client hotfix rollup as outlined in my previous blog post.
Forefront TMG 2010 Service Pack 2 Now Available
Service Pack 2 for Microsoft Forefront TMG 2010 is now available. In addition to numerous fixes released since SP1 and SP1 hotfix rollup 4, this service pack also includes the following new features:
New reports – A new site activity report that provides details about requests made to specific web sites for individual users.
New error pages – TMG SP2 provides the option to use new error pages that feature a whole new look and feel. In addition, these new error pages are more easily customized and can now include embedded objects.
Kerberos authentication for NLB – TMG SP2 includes the ability to leverage Kerberos authentication for clients accessing enterprise arrays via the NLB virtual IP address (VIP).
You can download Forefront TMG 2010 service pack 2 here. Please note that this update requires that Forefront TMG 2010 SP1 and software update 1 for TMG SP1 be installed prior to installing Forefront TMG 2010 SP2. Once TMG SP2 has been installed successfully the build number will be 7.0.9193.500.
For information regarding the installation of SP2 for Forefront TMG 2010 on enterprise arrays, click here.
Forefront TMG 2010 Firewall Client Hotfix Rollup – October 2011
A hotfix rollup for the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client is now available that resolves several issues reported on client systems with the TMG firewall client installed. They are:
KB2620156 – An active FTP data channel cannot be established for an internal computer that is running the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client.
KB2438187 – You cannot start a program that is installed many levels deep and that requires an Internet connection using the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client.
KB2620191 – Security update 2520426 causes a regression on a computer that is running the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client.
KB2620153 – A program experiences a 20-second delay when an established internal or external connection is closed when the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client is installed.
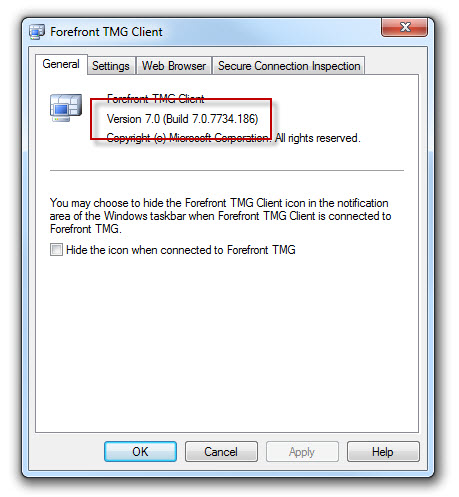
The Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client hotfix rollup can be downloaded here. After applying this hotfix rollup, the new Forefront TMG 2010 firewall client build number will be 7.0.7734.186.
Southern California IT Professionals Association September Meeting
On Thursday, September 8 2011, I will be presenting an overview of Microsoft Forefront edge security solutions at the Southern California IT Professionals Association monthly meeting. During the session I’ll be providing an overview of Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 and Unified Access Gateway (UAG) 2010, discussing common deployment scenarios, and highlighting the similarities and differences of the two solutions.
I will also be giving away copies of the Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 Administrator’s Companion and the Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG) 2010 Administrator’s Handbook. The event begins at 6:30PM PDT and will be held at the CSU Fullerton campus in Irvine. For more information and to RSVP for the event, click here.
Hope to see you there!
Access to the Web Proxy Filter on Forefront TMG 2010 is Denied
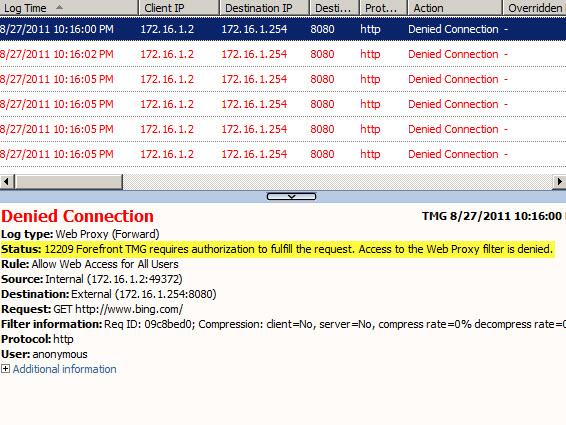
Frequently I am asked to review Forefront TMG 2010 firewall logs for suspicious behavior. Often times a security administrator will express concerns about many instances of denied requests by clients attempting to connect to Forefront TMG’s web proxy service. On busy TMG firewalls there may be hundreds or even thousands of instances where the following access denied record appears in the Web Proxy logs:
Status: 12209 Forefront TMG requires authorization to fulfill the request. Access to the Web Proxy filter is denied.
On a Forefront TMG 2010 firewall where web access rules require authentication, this behavior is expected and by design. It does not indicate an attack of any type on the Forefront TMG firewall or its web proxy service. The root cause for the flood of access denied messages has to do with how the Web Proxy client behaves when accessing resources via an authenticating web proxy like the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall. When a Web Proxy client sends its initial request for a resource it will always attempt to do so anonymously. Only when prompted for authentication by the firewall will the web proxy client provide the credentials of the logged on user.
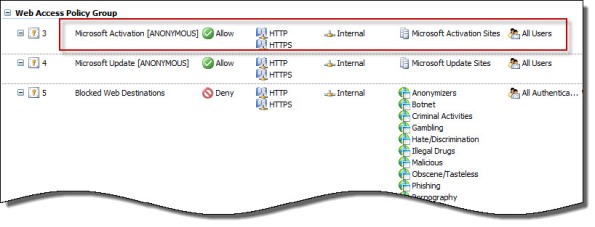
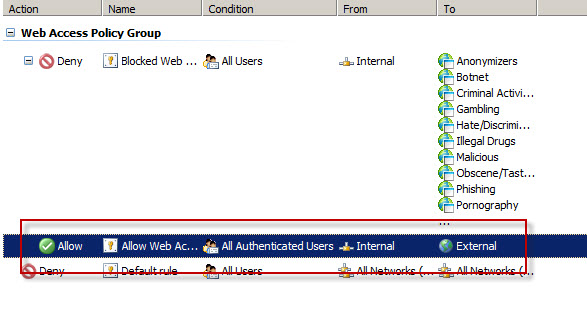
Consider a scenario where Forefront TMG is configured to only allow authenticated users to access the Internet. The firewall policy might look something like this:
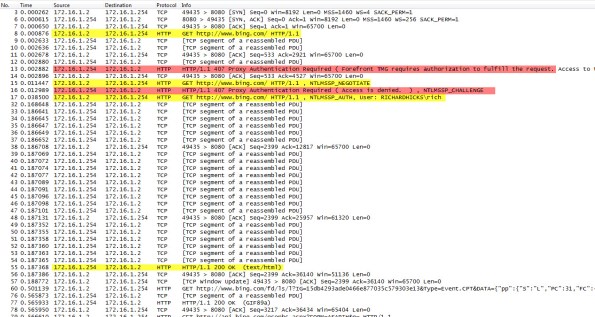
Below is a network trace taken from a client attempting to access http://www.bing.com/ through a TMG firewall as configured above.
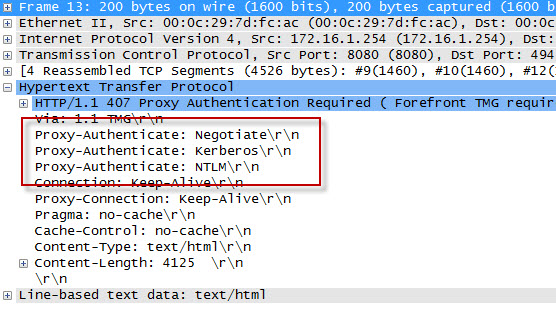
We can see that the first three packets of the trace are the TCP three-way handshake taking place between the web proxy client and the Forefront TMG firewall. Once a connection to the web proxy listener has been established, in packet 8 the client sends an HTTP GET request for http://www.bing.com/. In packet 13 you’ll see that the Forefront TMG firewall denied the request and replied with an HTTP 407 response, indicating that proxy authentication was required. This was done because the Forefront TMG firewall did not have any access rules which would allow the anonymous request. It did, however, have access rules that might apply to this request, depending on who the user is. This response also includes which authentication methods the web proxy listener is configured to accept.
In packet 15 the web proxy client again submits its HTTP GET request for http://www.bing.com/, this time indicating that it would like to use the NTLM Secure Service Provider (SSP). In packet 16 the Forefront TMG web proxy denies the request yet again and replies with another HTTP 407 response, this time including the NTLM challenge. In packet 17 the client submits an HTTP GET request for http://www.bing.com/ and supplies the credentials in the form of an NTLM response.
As you can see, each time a web proxy client requests a resource through a Forefront TMG firewall that requires NTLM authentication the client is actually denied twice during the transaction before being successfully authenticated and allowed access. If this sounds like a lot of overhead for authenticated proxy traffic, you are right. Denying each request twice consumes additional resources on the Forefront TMG firewall and introduces some latency for clients as well. In addition, the burden of authenticating the user is placed on the TMG firewall when using NTLM, as the firewall itself must contact a domain controller to authenticate the user. You can reduce the authentication load on the Forefront TMG firewall considerably by enabling Kerberos authentication. When the Forefront TMG firewall is configured to use Kerberos there is only a single denied request and HTTP 407 response. The client must then contact a domain controller and obtain a Kerberos ticket to present to the TMG firewall to gain access to the resource. Information on how to configure Microsoft ISA Server and Forefront TMG 2010 to use Kerberos authentication can be found here.
Additional information…
HTTP response codes – http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html
NTLM challenge/response – http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NTLM
Forefront TMG 2010 Network Inspection System and Custom Protocols
An intrusion detection and prevention system (IDS/IPS) is an essential component of a modern secure web gateway. The Network Inspection System (NIS) in Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 is a unique implementation of IDS/IPS. NIS is focused specifically on detecting and preventing attacks on Microsoft operating systems and applications. NIS uses signatures that are developed by the Microsoft Malware Protection Center (MMPC) and are distributed through Windows Update or WSUS.
NIS in Forefront TMG 2010 provides protection by performing low-level network protocol inspection. Each packet is analyzed for protocol state, message structure, and message content. When a packet is received, NIS will inspect it only after the firewall policy has allowed it, and only after any associated web or application filters have processed it.
There is one caveat, however. A custom protocol is not subject to NIS inspection by the Forefront TMG firewall unless it is associated with a standard protocol. Often a Forefront TMG firewall administrator will create a custom protocol for a standard protocol that uses a non-standard port. One of the most common protocols to be configured to use non-standard ports is the HTTP protocol. For example, if an administrator defines a custom protocol to support a web-based application that uses the non-standard TCP port 62112, by default NIS will not inspect this traffic even though the communication is HTTP, a protocol which NIS normally inspects when it takes place over the standard TCP port 80.
To apply Forefront TMG NIS inspection to a custom protocol it must first be associated with a standard protocol. In our example we’re using HTTP over a non-standard port, so we need to associate our custom protocol with the Web Proxy Filter.
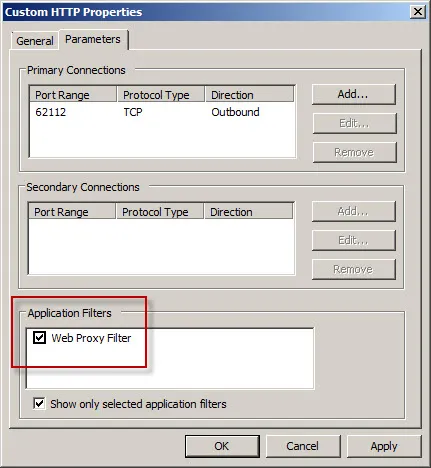
Next, associate the custom protocol with a standard protocol definition, in this case HTTP Proxy.
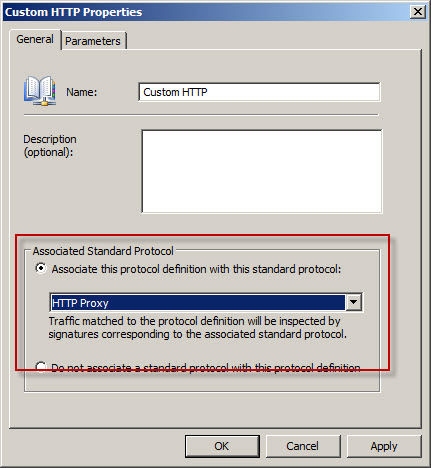
Once complete, Forefront TMG NIS inspection will be applied to the custom protocol and policy will be enforced according to the current NIS configuration.
Forefront TMG NIS additional information: