Archive
Configuring Splunk Universal Forwarder on Forefront TMG 2010
Aggregating logged data from security devices such as the Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 firewall is a top priority for many security engineers. Forefront TMG and its predecessor, ISA Server, have always lacked an integrated facility to forward logged data to an external event management system. Often the administrator will have to devise an elaborate process that consists of batch files or scripts that collect firewall and web proxy logs and copy them to another location where they can be consumed. In the past I’ve demonstrated how third-party utilities can convert firewall log data to the syslog format as well.
Splunk is one of the more popular log management systems in use today, and to make it easier to get Forefront TMG log data in to Splunk we can use the Splunk Universal Forwarder. The Universal Forwarder is a utility that installs on the Forefront TMG firewall and monitors the folder containing W3C formatted text log files. The Universal Forwarder has a small footprint and consumes few resources, making it the ideal method to collect Forefront TMG log data and deliver it to the Splunk indexing server for analysis and archiving. The Splunk Universal Forwarder can be downloaded here.
Configuring Forefront TMG 2010
Before installing the Universal Forwarder, the Forefront TMG firewall must be configured to log to text file format. To change the log file format, open the Forefront TMG management console and highlight the Logs & Reports node in the navigation tree, select the Logging tab in the center console window, and then click Configure Firewall Logging in the Tasks pane on the right.
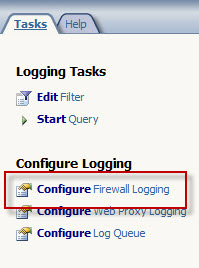
Select the option to log to File and choose the W3C extended log file format from the drop down box below. Repeat these steps to configure web proxy logging.
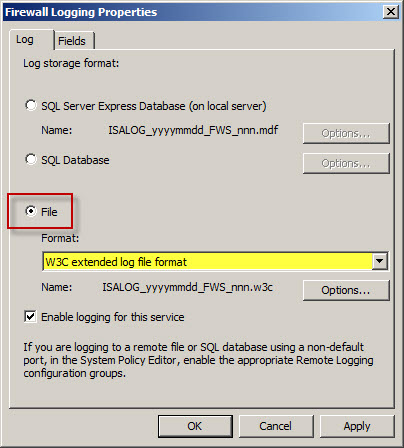
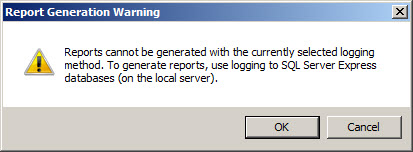
When the option to log to text file format is chosen, native Forefront TMG reports cannot be generated and access to historical log data in the Forefront TMG management console is no longer possible. Clicking Ok will generate the following warning message:
Reports cannot be generated with the currently selected logging method. To generate reports, use logging to SQL Server Express databases (on the local server).
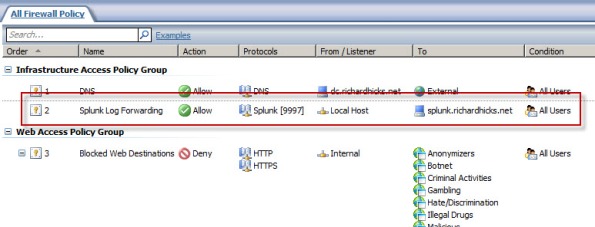
An access rule must be created to allow the Splunk Universal Forwarder to communicate with the Splunk indexing server. The source will be the local host network, the destination will be the Splunk indexing server, and the protocol will be TCP 9997 (outbound), which is the default port used by the Splunk Universal Forwarder.
Configuring Splunk Universal Forwarder
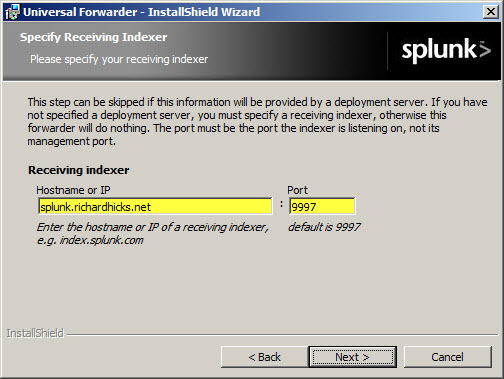
Next, install the Splunk Universal Forwarder on the Forefront TMG firewall. When prompted, enter the hostname, FQDN, or IP address of your indexing server and specify a TCP port to use (the default is TCP port 9997).
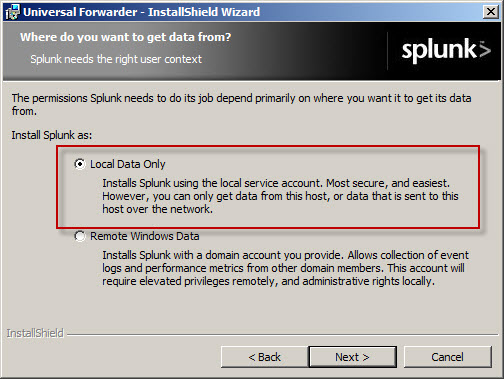
Select the option to forward Local Data Only.
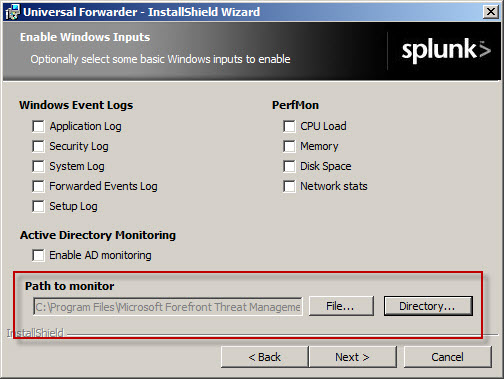
The Forefront TMG firewall will create new text log files each day and store them in the specified log files folder. Specify a Path to monitor by clicking Directory… and selecting C:\Program Files\Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway\Logs (or the path where your log files are stored, if different from the default).
Configure Splunk Indexing Server
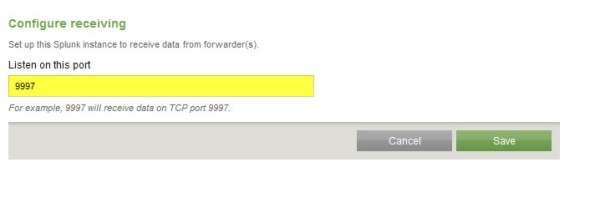
Once the installation is complete, open the Splunk Manager and click Forwarding and receiving.
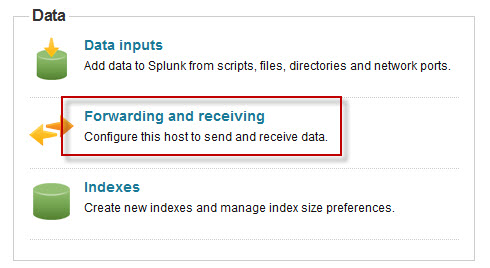
Click the Add new link next to Configure receiving.
Configure the indexing server to Listen on this port and enter 9997.
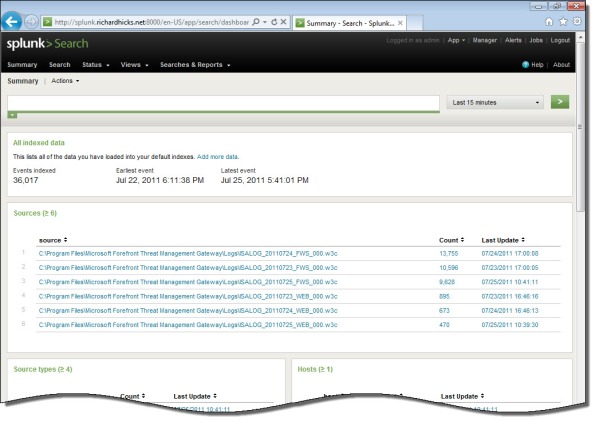
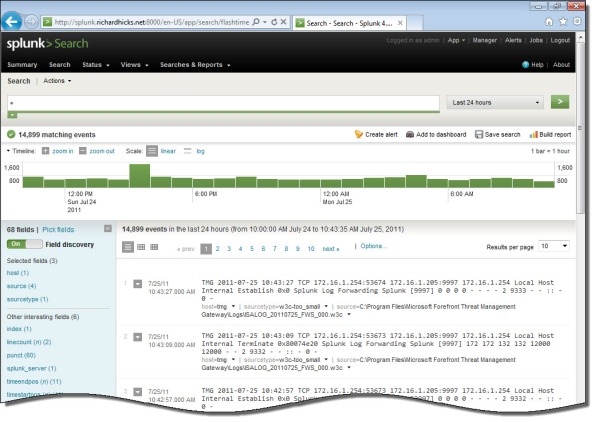
Once you’ve configured Splunk to receive data from the forwarder, Forefront TMG firewall and web proxy log data should appear on the indexing server.
Integrating Websense Web Security and Web Filter v7.6 with Forefront TMG 2010
For customers currently running Microsoft ISA Server 2004 or 2006 with integrated Websense Web Security or Web Filter, the options for migrating to Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 have historically been limited. Until recently, Websense provided only limited support for integrating with Forefront TMG. However, beginning with the release of Websense Web Security/Web Filter v7.6, Websense now provides full support for integrating with Forefront TMG 2010 running on the latest Windows Server 2008 R2 operating system.
Integrating Websense Web Security/Web Filter with Forefront TMG is accomplished by installing the Websense filtering plug-in on the TMG firewall. The plug-in will communicate with external Websense components to provide URL filtering capabilities. Before installing the Websense filtering plug-in on the TMG firewall, install the Websense infrastructure and Web Security/Web Filter components (policy server, policy broker, filtering service, etc.) on a separate system.
Note: This post is intended to provide installation and configuration tips for firewall administrators who wish to integrate Websense Web Security/Web Filter v7.6 with Forefront TMG 2010. It is not meant to be a comprehensive Websense installation guide. For more information on installing and configuring Websense Web Security/Web Filter v7.6, please refer to the Websense Deployment and Installation Center documentation provided by Websense.
Policy/Filtering Server
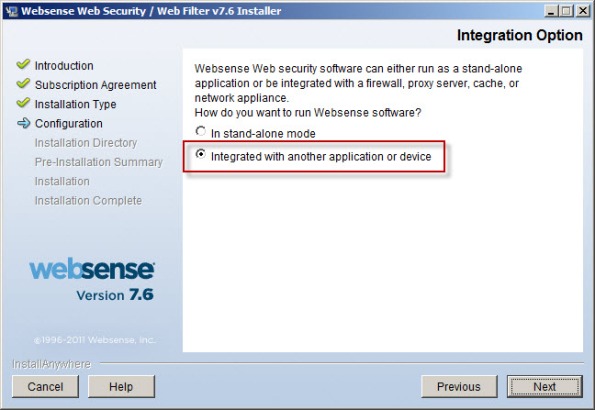
When installing the Websense Web Security/Web Filter components, be sure to select the option to integrate with another application or device.
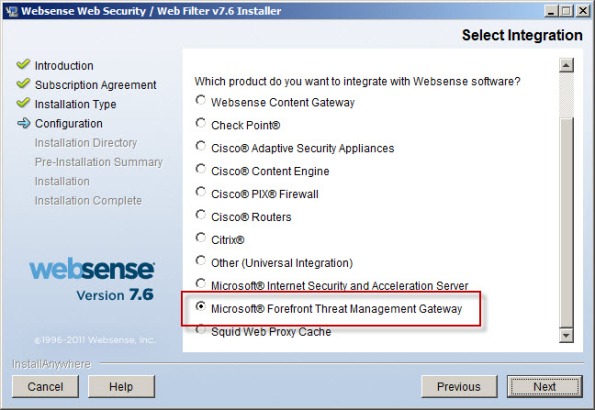
Scroll down and select Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway.
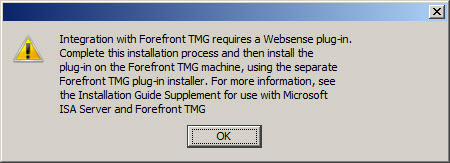
The installer will remind you that integrating with Forefront TMG requires a separate Websense plug-in to be installed on the TMG firewall.
Integration with Forefront TMG requires a Websense plug-in. Complete this installation process and then install the plug-in on the Forefront TMG machine, using the separate Forefront TMG plug-in installer. For more information, see the Installation Guide Supplement for use with Microsoft ISA Server and Forefront TMG.
Filtering Plug-In
Note: The filtering plug-in for Forefront TMG 2010 is available as a separate download apart from the Websense Web Security/Web Filter v7.6 installer. It can be downloaded after logging in to my.websense.com.
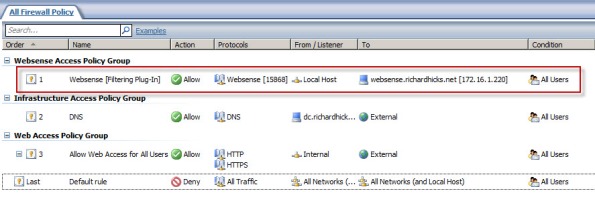
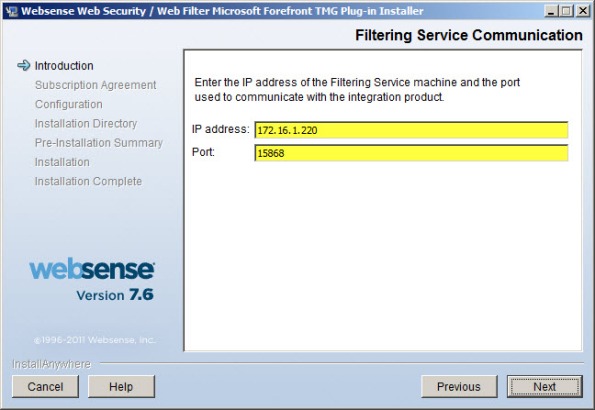
An access rule is required to allow the filtering plug-in to communicate with the Websense filtering service. Before installing the plug-in, create a rule on the Forefront TMG firewall allowing the local host network to communicate with the Websense policy/filtering server on TCP port 15868.
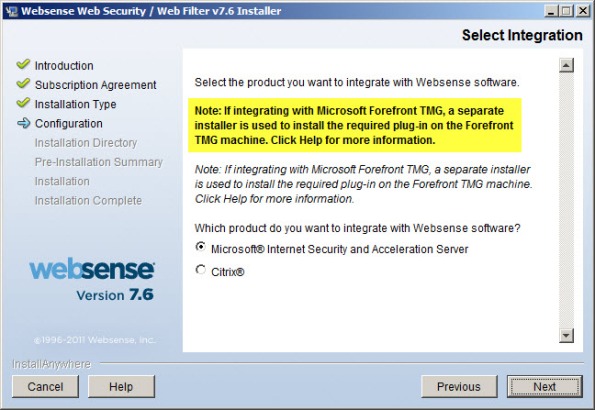
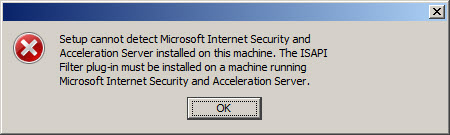
If you attempt to use the Websense Web Security/Web Filter v7.6 installer to install the filtering plug-in on the Forefront TMG fireall, you will only see the option to integrate with Microsoft ISA Server. If you continue anyway, the installation wizard will prompt with the following reminder:
Note: If integrating with Microsoft Forefront TMG, a separate installer is used to install the required plug-in on the Forefront TMG machine. Click Help for more information.
If you proceed, the installation wizard will stop and generate the following error message:
Setup cannot detect Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server installed on this machine. The ISAPI Filter plug-in must be installed on a machine running Microsoft Internet Security and Acceleration Server.
Once you have downloaded the Websense filtering plug-in for Forefront TMG, installation is simple and straightforward. Run the installation wizard and provide the IP address of the Websense policy/filtering server and accept the default port.
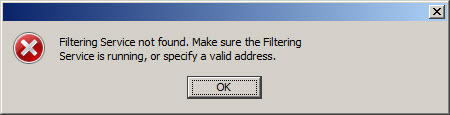
If the Websense policy/filtering server is not reachable or unavailable you will receive the following error message:
Filtering Service not found. Make sure the Filtering Service is running, or specify a valid address.
Verify that you have specified the correct IP address for the policy/filtering server, that it is online and reachable, and that your access rule is configured correctly.
During the plug-in installation process it is necessary to stop the Forefront TMG firewall service. Remember that stopping the Forefront TMG firewall service will place the firewall in lockdown mode, preventing normal Internet access. You can stop the firewall service by using the Services MMC, or you can simply open an elevated command prompt and issue the following command:
net stop fwsrv
After the plug-in has been installed successfully you can restart the firewall service by issuing the following command:
net start fwsrv
For Forefront TMG 2010 Enterprise arrays, the Websense Web Security/Web Filter plug-in must be installed on each array member. Once you’ve completed the installation of the Websense filtering plug-in you should now be able to create, apply, and enforce URL filtering policies using the Websense management console.
Additional Notes
Don’t forget to ensure complete filtering coverage for Forefront TMG SecureNAT and Firewall clients by creating the ignore.txt file in C:\Windows\System32 that includes the hostname of the TMG firewall in UPPERCASE. For enterprise arrays this must be completed on each array member.
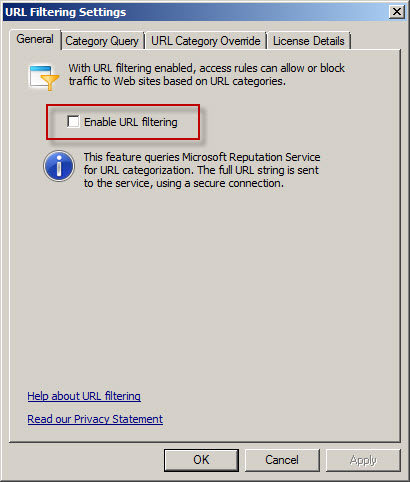
Another important point to remember is that the native Forefront TMG URL filtering must be disabled with integrated Websense Web Security/Web Filter v7.6 to prevent unexpected behavior. You can disable TMG URL filtering by highlighting the Web Access Policy node in the navigation tree, then clicking the Configure URL filtering link in the Tasks pane and unchecking the option to Enable URL filtering.
Virus/malware scanning, Network Inspection System (NIS), and HTTPS inspection are all compatible with Websense Web Security/Web filter v7.6, and having these features enabled is highly recommended to provide the most complete protection.
If you have to uninstall the Websense filtering plug-in for any reason, be sure to use the Add/Remove programs control panel applet. Removing the filter manually will cause problems for the Websense policy and filtering server. Do not remove the filter manually or reset your appliance image/VM snapshot without uninstalling the plug-in first to avoid these issues.
Security Configuration Wizard for Forefront TMG 2010 and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1
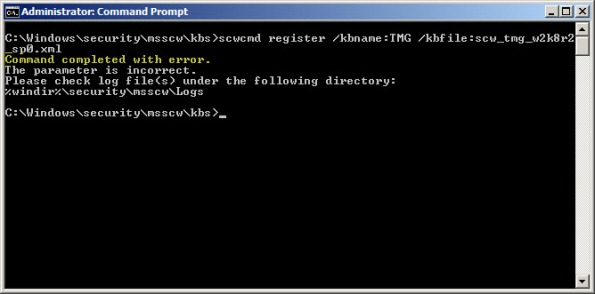
Security hardening and attack surface reduction is an important step in preparing a Forefront TMG 2010 firewall. To accomplish this task, the tool of choice is the Security Configuration Wizard (SCW). In one of my ISAserver.org articles I demonstrated how to use this tool to properly configure the underlying operating system to support the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall role. Since the native Windows SCW does not include support for the Forefront TMG role, the TMGRolesForSCW.exe utility included in the Forefront TMG Tools and SDK is required. This tool was released prior to service pack 1 for Windows Server 2008 R2 and does not include a template that works correctly out of the box. When you attempt to register the Windows Server 2008 R2 template on a system with SP1 installed you will receive the following error:
Command completed with error. The parameter is incorrect. Please check log file(s) under the following directory: %windir%\security\msscw\logs
To resolve this issue, create a copy of the template file SCW_TMG_W2K8R2_SP0.xml and name it SCW_TMG_W2K8R2_SP1.xml. Open this file with any text editor and navigate to the SCWKBRegistrationInfo node (line 2). Change the value of ServicePackMajorVersion from “0” to “1” and save the file. Register the template using the following command:
scwcmd register /kbname:TMG /kbfile:scw_tmg_w2k8r2_sp1.xml
Continue using the SCW to configure and apply a security template to your TMG firewall following the instructions in my ISAserver.org article.
Vulnerability in the Forefront TMG 2010 Client Could Allow Remote Code Execution
It is extremely rare to see a security update for anything relating to the Forefront TMG firewall. However, the June 2011 security bulletin includes update MS11-040 that addresses a privately reported vulnerability in the Forefront TMG client that could allow remote code execution. This security update applies only to the Forefront TMG client, not the firewall itself. Also, it does not apply to previous versions of the ISA firewall client.
Before applying the MS11-040 update, the latest version of the Forefront TMG client was build 7.0.7734.100. After applying the MS11-040 update, the new build number will be 7.0.7734.182.
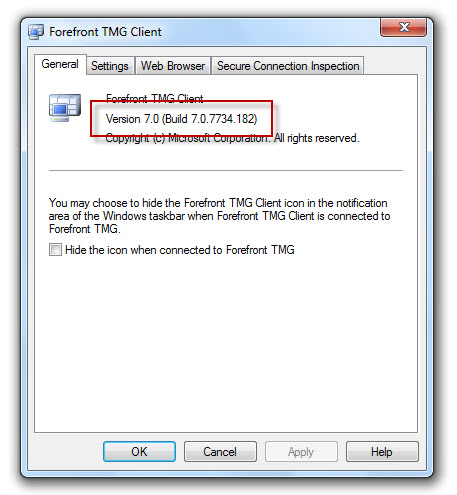
Forefront TMG 2010 Web Proxy Auto Detect Fails
Recently I received a call from a customer who was trying to resolve an issue where all web proxy clients that were configured to use Web Proxy Auto Discovery (WPAD) with DNS suddenly stopped working. We began troubleshooting by confirming that the hostname WPAD resolved to the internal IP address of the Forefront TMG firewall, which it did correctly. Next we used a telnet client to confirm that the TMG firewall was listening on TCP port 80 (used by TMG for DNS WPAD clients) and indeed it was responsive. A scan of the event logs on the firewall turned up the following warning message:
“The Web Proxy filter failed to bind its socket to 172.16.1.253 port 80. This may have been caused by another service that is already using the same port or by a network adapter that is not functional. To resolve this issue, restart the Microsoft Firewall service. The error code specified in the data area of the event properties indicates the cause of the failure.”
Something was listening on TCP port 80, so we opened a command prompt and entered the following command in order to determine which process was listening on this port:
netstat –ano | findstr :80
Netstat was reporting that TCP port 80 was in a listening state and bound to the IP address 172.16.1.253. The process using this port was the System process (PID 4). This is unexpected, because the Forefront TMG web proxy service (wspsrv.exe) should be bound and listening on this port. Clearly this was a web service hijacking this port, so to find out more we entered the following command at a command prompt:
netsh http show servicestate
The output of this command revealed a valuable clue. Notice the registered URL below…
HTTP://172.16.1.253:80:172.16.1.253/REPORTSERVER_ISARS/
As it turns out, this customer had attempted to change the SQL Reporting Services Web Service URL. By assigning the Forefront TMG firewall’s internal IP address and changing the port to 80 in the Reporting Service Configuration Manager, this caused a conflict with the Forefront TMG web proxy filter, which requires TCP port 80 to provide WPAD for DNS.
To resolve the issue, the administrator chose a TCP port other than 80 and restarted the system.
Relocating SQL Database Files on Forefront TMG 2010
When Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 is installed, an instance of SQL Server 2008 Express is included for Forefront TMG firewall and web proxy logging. By default, the log database files are installed on the system partition, which is less than ideal. Best practices dictate that log database files should reside on a separate, dedicated partition.
I’ve had many people ask how to move these database files once the product is installed. Most assume that the process involves using SQL database management tools to detach the database and manually move the database files to a new partition. Not true! Since Forefront TMG handles all of the underlying SQL database management, the process is actually quite simple.
To move the log database files, first create a folder to store them in the new location. Next, open the Forefront TMG management console, highlight Logs & Reports in the navigation tree, select the Logging tab in the center console window, then click Configure Firewall Logging in the Tasks pane on the right.

Click the Options… button, then select This folder (enter the full path): and enter the new path to store the log database files.

For EMS-managed or standalone arrays, make certain this path exists on each array member. If it does not, the service will not start. If the folder does not exist, TMG will complain.

Repeat this process to move the web proxy log database files. In addition, it would be an excellent idea to also move the Log Queue Storage Folder. This folder should be located on a partition that is separate from the one used to store the log database files. For optimum availability this will be a separate physical disk, allowing for Forefront TMG to continue logging to the queue even in the event of a physical disk failure where the log database files are stored. As with the log database files, this folder must exist on each array member.

A system variable can be used to specify the path to log database or log queue files. For example, %LOGDRIVE%\FWS, where %LOGDRIVE% can be a different drive letter and path on each array member, if necessary. To create a system variable, open the advanced system properties and click Environment Variables….

Under System variables click New…, enter the variable name (e.g. LOGDRIVE), and specify the location where the log files should be stored on this array member (e.g. D:\TMGLogs). Repeat these steps on each array member, specifying the local path where log database files are to be stored.

Confirm the system variable was created properly by opening a command prompt and entering the following command:
set logdrive
The output for our example should appear as follows:
LOGDRIVE=D:\TMGLogs
Network Egress Filtering and the RSA SecurID Attack
Reading details about the recent attack and compromise at SecurID, I was dumbfounded when I came across the following:
“The attacker then used FTP to transfer many password protected RAR files from the RSA file server to an outside staging server at an external, compromised machine at a hosting provider. The files were subsequently pulled by the attacker and removed from the external compromised host to remove any traces of the attack.”
I’m not surprised at all that an attacker was able to infiltrate the RSA private network. However, with this and myriad similar attacks I’ve read about over the past few years, one thing that consistently amazes me is the relative ease with which attackers can get back out.
It appears in this case that RSA allows outbound FTP to anywhere on the Internet. Clearly this is not good security practice. This is not to say that an attacker couldn’t use another channel to exfiltrate stolen data, but having such generous outbound access rules for file transfer protocols makes it that much easier for the criminals.
To provide better protection from these types of attacks, security policy should be updated to disallow unrestricted outbound FTP access to the general Internet. Following the principle of least privilege, outbound FTP access should be granted only to certain users and to specific sites, and only after it is determined there is a business requirement for such access. This access should be reviewed on a periodic basis.
Using Forefront TMG 2010 and leveraging the TMG Firewall Client, it is possible to create outbound FTP access rules and enforce user and group authentication. Although this won’t necessarily prevent an attacker from uploading data through the gateway, it presents yet another hurdle for the attacker to clear in order to extract data. If the attacker is still successful, the access logs on the Forefront TMG firewall will include valuable forensic data, including the name of the application used to transfer data and the account information used by the attacker, in addition to the usual log detail (e.g. source and destination IP addresses, etc.).
State-of-the art perimeter defense technology is not enough. Security policy and strong network egress filtering are essential to prevent data loss. I’d suggest reviewing your outbound access policies today.
Preparing Forefront TMG 2010 for Enterprise Workgroup Deployment
Deploying Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 in a workgroup (non-domain joined) enterprise array configuration can present a significant challenge to many administrators. This post isn’t meant to be a comprehensive TMG Enterprise Management Server (EMS) deployment guide, but I would like to share with you a few important tips that will hopefully make the process of creating an EMS-managed array a little easier.
Before Installing EMS
IP Addressing – Make certain that all basic IP connectivity is verified before installing any Forefront TMG 2010 services.
Name Resolution – Confirm that name resolution is working properly and that hostnames are being resolved to the correct IP addresses. Be sure that these IP addresses are assigned to the Internal network interface of the EMS and each array member.
Certificates – The EMS will require a machine certificate, and each array member should trust the Certificate Authority (CA) that issued this certificate. It is recommended that this certificate be issued by your internal private CA and not a public third-party CA. The certificate should be for server authentication and the common name on the certificate should be the FQDN of the host it is to be installed on. Be sure to install the root certificate and any intermediate certificates for the CA on the EMS and each array member. Make certain the certificate is issued with the option for the private key to be exportable.
Local Accounts – Identical (mirrored) local accounts should be configured on the EMS and each array member and be granted administrative rights for the Forefront TMG 2010 Enterprise.
After Installing EMS
Before joining a TMG firewall to an array, you can perform some preliminary tests to determine if certificate authentication between hosts is working correctly. To do this, open a PowerShell command window and enter the following commands:
import-module servermanager add-windowsfeature rsat-adlds
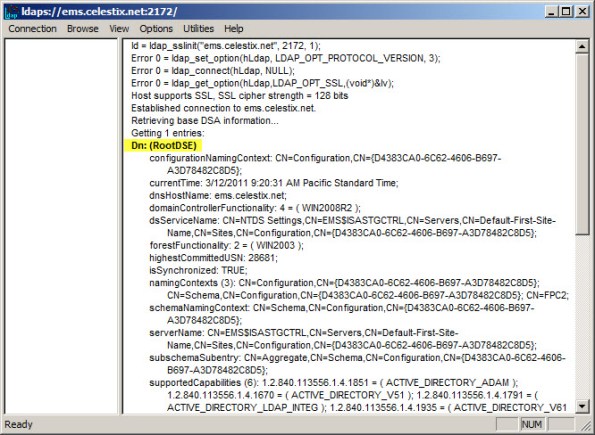
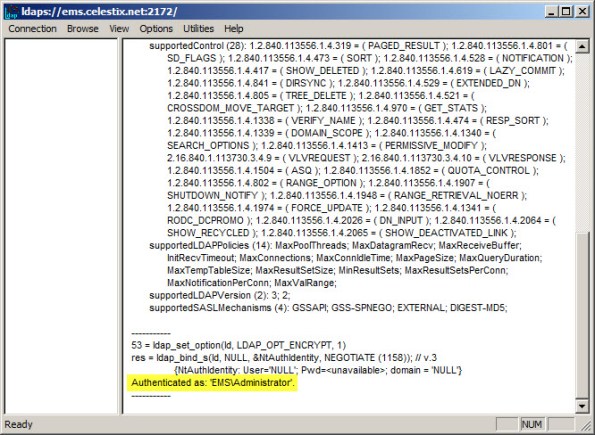
Once complete, click Start | Run and enter ldp.exe. From the drop-down menu choose Connection, and then Connect…. For the server, enter the fully-qualified domain name (FQDN) of the EMS, specify port 2172, and then select the option to use SSL.
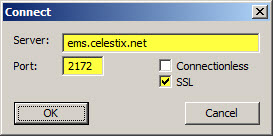
If certificate authentication is working correctly you will connect to the RootDSE. If it is not configured correctly you will receive a connection error.
To determine if user authentication is working correctly, select Connection from the drop-down menu and then Bind…. If you are currently logged on with the local mirrored account, select the option to Bind as currently logged on user, otherwise select Bind with credentials and enter the user and password of the mirrored account (leave the domain blank).
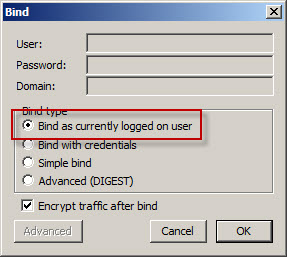
If configured correctly you will receive notification that you have been authenticated. If not, you will be notified that the logon attempt failed.
Once you’ve completed these steps you can proceed with configuring the TMG firewall to join the array. Be sure to specify the name of the EMS in exactly the same format as the certificate common name (preferably using the FQDN ).
Phoenix Unified Communications User Group
Are you interested in learning how Forefront Threat Management Gateway (TMG) 2010 can protect your Microsoft Exchange implementation? If so, join me at the Phoenix Unified Communications User Group meeting at 4:00PM on Wednesday, March 30 2011 in Tempe, AZ where I’ll be presenting on the topic. We’ll discuss how to leverage TMG to protect Outlook Web App, Exchange ActiveSync, OutlookAnywhere, and SMTP communication. This month’s meeting is being held at the new Microsoft building. The address is:
Microsoft Corporation
60 E. Rio Salado Parkway
12th Floor
Tempe, AZ 85282
[map]
You can register for the event here. Hope to see you there!

Forefront TMG Performance Troubleshooting with PAL v2.x Part 2 – Data Analysis and Reporting
In the first part of this two-part series we used PAL and Performance Monitor to collect data. In this second part I’ll demonstrate how to use PAL to analyze the data and generate a report.
Analyzing the Data
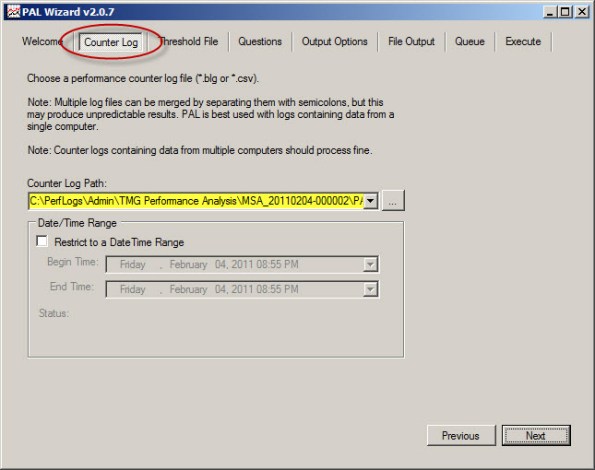
Once you’ve collected the necessary log data you are ready to analyze it using PAL. To begin, open the PAL tool, click Next or select the Counter Log tab, then choose the path to the log file collected using Performance Monitor.
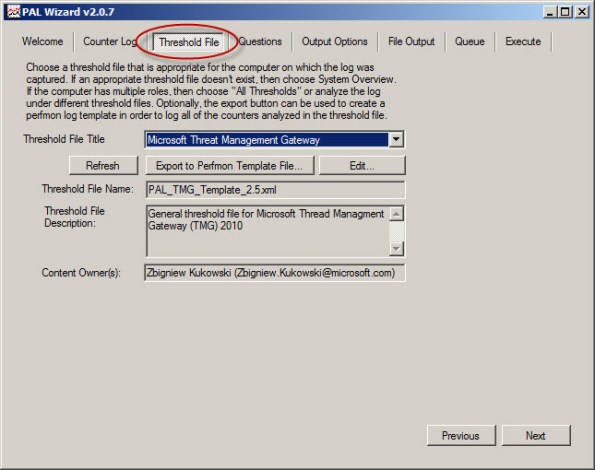
Select Microsoft Forefront Threat Management Gateway for the threshold file and choose Next.
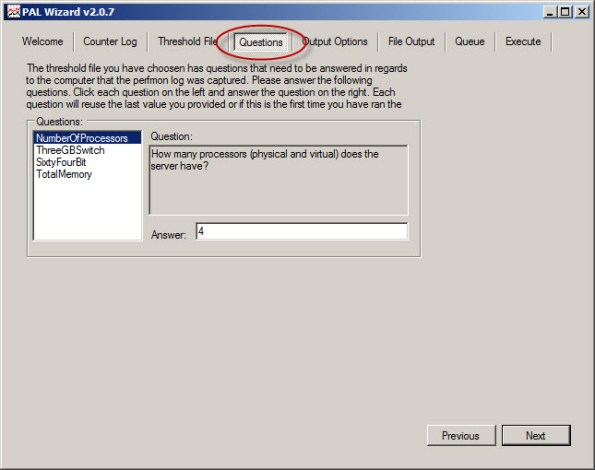
To accurately analyze the data, PAL needs to know specific details about the system where the log data was collected. Highlight and answer each question and choose Next.
Accept the default settings for Analysis Interval and All Counter Stats.
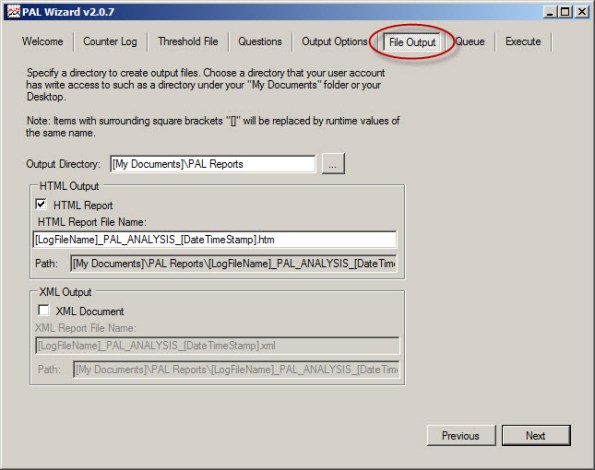
By default, PAL generates reports in HTML format and places them in the My Documents\PAL Reports folder. Here you can change the default file location and also select the option to generate reports in XML format.
Behind the scenes PAL leverages a complex PowerShell script to perform analysis and generate reports.
To perform the analysis and generate a report, click Finish. Optionally you can add the analysis job to the job queue or execute the analysis and restart the wizard with the same settings. You can also select the option to execute as a low priority process.
PAL begins analyzing the log data and once complete it generates a report in the format specified. You can view a sample report here.
The report is very detailed and includes alerts when a particular counter exceeds a predetermined threshold. The alerts are color coded to easily identify when a threshold has been exceeded. The report also includes a brief explanation of each counter, a graphical chart of the data analyzed, and statistical data relating to the counter.
PAL is a wonderful tool that greatly simplifies the process of analyzing Performance Monitor data. It is not, however, a magic wand that will solve all of your performance issues automatically. Although the tool provides a wealth of information in a clear and concise format, it is still up to the administrator to understand the data and ultimately determine how best to resolve the issue. PAL just makes that task much easier.
Forefront TMG Performance Troubleshooting with PAL v2.x Part 1 – Data Collection
Forefront TMG Performance Troubleshooting with PAL v2.x Part 2 – Data Analysis and Reporting