Archive
July 2012 Twitter Outage and Forefront TMG URL Filtering
Earlier today Twitter suffered a serious outage. To further complicate matters, it appears that Microsoft Reputation Services (MRS) is now categorizing twitter.com as a phishing site.


I’m not certain what the reason for this categorization is for, but based on past experience it may have to do with Twitter services running on a shared hosting provider that previously included services that were identified as phishing related. To resolve this issue, open the Forefront TMG management console, highlight the Web Access Policy node in the navigation tree, then click Configure URL Category Overrides in the Tasks pane and move the URL pattern *.twitter.com/ to the Online Communities category.

Forefront TMG 2010 Update Center Quick Tip
The Update Center in the Forefront TMG 2010 management console provides an instant view of the status of signature updates for the Malware Inspection and Network Inspection System (NIS) protection mechanisms. However, the column layout leaves out important information that can be essential when troubleshooting signature update issues. By default, the Last Checked and Last Success columns are hidden from view. To display these details, right-click anywhere in the column headings and then select Add/Remove Columns.
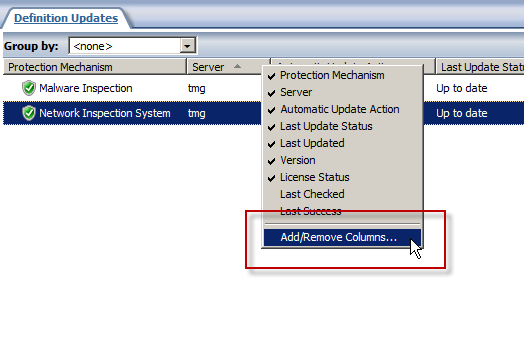
Next, select the Last Checked and Last Success columns and click Add.

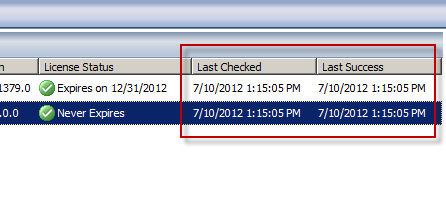
Now you’ll see when the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall last checked for updates and when it was last successful.
Disable Logging on System Policy Rules in Forefront TMG 2010
I’ve written a number of articles on improving system performance and logging optimization over the years. As I’ve mentioned previously, this involves the security administrator reviewing each access rule and deciding if the traffic is interesting enough to require logging. If it is not, to improve performance and reduce log pollution it is advisable to disable logging for the access rule in question.

However, when attempting to make this change to a system policy rule you will encounter the following error:
The changes cannot be saved. Error: 0xc0040334 This property cannot be modified for the predefined item. The error occurred on object <policy rule name> of class ‘Policy Rule’ in the scope of array .

Unfortunately the system policy editor provides no facility to make this change in the GUI. To work around this limitation you can use COM to disable logging on system policy rules programmatically using the following script. In this example I’ve chosen to disable logging on the Allow intra-array communication system policy rule.
Option Explicit
Dim Root, Array, Rule
Set Root = CreateObject("FPC.Root")
Set Array = Root.GetContainingArray()
Set Rule = Array.SystemPolicy.PolicyRules.Item("Allow intra-array communication")
Rule.EnableLogging = False
Rule.Save
WScript.Echo “Done!”
Set Rule = Nothing
Set Array = Nothing
Set Root = Nothing
Note: To see this change reflected in the management console, hit F5 to refresh or close and reopen the console.
If you wish to disable logging for all system policy rules, alter the script to use a For Each Next construct as follows:
Set Rules = Array.SystemPolicy.PolicyRules For Each Rule in Rules Rule.EnableLogging = False Next
Forefront TMG and UAG 2010 Presentation at TechEd North America 2012
For those of you who were not able to attend Microsoft TechEd North America 2012 this year, the session I presented entitled “Demystifying Microsoft Forefront Edge Security Solutions: TMG and UAG” is now available online. Enjoy!
Forefront TMG 2010 Guest Blogging for Fastvue
Recently I was given the opportunity to write some guest blog posts about Forefront TMG 2010 for Fastvue. Fastvue develops TMG Reporter, an excellent real-time dashboard, alerting, and reporting tool that integrates with Forefront TMG 2010. Be sure to check out these new articles that have been posted:
Logging Improvements in Forefront TMG 2010
Enterprise Reporting Challenges with Forefront TMG 2010
Tips for Healthy Logging and Reporting in Forefront TMG 2010
Forefront TMG 2010 Enterprise Logging with Remote SQL Server
TMG Reporter is a significant upgrade from the native reporting tools included with Forefront TMG 2010. Download a free evaluation of their software today and give it a try. You won’t be disappointed!
Forefront TMG 2010 Account Lockout Feature for FBA
Consider a scenario in which you have published your Exchange 2010 Outlook Web App servers using Forefront TMG 2010 and are using Active Directory or LDAP authentication along with Forms-based Authentication (FBA). In an effort to gain access to the system, an attacker may perform a brute force password attack by either manual or programmatic means. The attacker will attempt to guess the password for a given user until they reach the configured account lockout threshold as defined in Active Directory. Once this happens, the attacker will have to wait for the password to unlock automatically or be unlocked by an administrator depending on your security policy. Effectively this results in a Denial of Service (DoS) because the legitimate user is unable to authenticate when this happens.
To address this concern, Forefront TMG SP2 includes a feature that allows administrators to enforce an account lockout policy on the Forefront TMG firewall itself. When configured with thresholds lower than those configured in Active Directory, this feature provides valuable protection from DoS that result from unsuccessful password guessing attempts. To enable this feature, install Forefront TMG 2010 SP2, and then follow these detailed instructions.
Controlling Access to File Shares with Forefront TMG 2010
Consider a scenario in which you have an IIS server located in a perimeter network protected by Forefront TMG 2010. The server is published to the Internet and is used to display product information for your company. Web content developers on your internal network need to have access to file shares on the IIS server to upload new web content. To facilitate this access you create an access rule to allow CIFS access to the IIS server. For security reasons you decide to restrict access to members of the Web Content Developers domain group. In addition, your workstations have the Forefront TMG Firewall Client installed. The access rule looks like this:
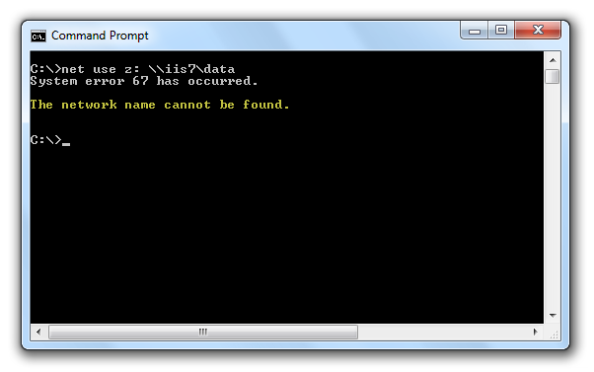
When users attempt to map a drive to the file share on the web server they receive the following error message:
System error 67 has occurred. The network name cannot be found.
In addition, the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall log indicates the following:
Denied Connection Log Type: Firewall Service Status: The action cannot be performed because the session is not authenticated.

At this point you might be puzzled because you have the Forefront TMG Firewall Client is installed on the workstation. TMG Firewall Client communication is always authenticated, so why does the firewall log indicate otherwise? The answer is simple. The Forefront TMG 2010 Firewall Client is a Layered Service Provider (LSP) that listens for Winsock calls made by the operating system and applications. Any Winsock calls made for resources on a remote network will be transparently delivered to the proxy server by the Firewall Client. However, CIFS communication does not use Winsock, so the TMG Firewall Client does not handle this traffic. As such, the network requests are delivered to the Forefront TMG firewall as SecureNAT requests. Since the rule in question requires authentication, and SecureNAT traffic cannot be authenticated, the firewall appropriately denies the traffic and the request fails.
You can resolve this issue by removing authentication on the access rule and controlling access on the file share itself. If you want to enforce user and group authentication at the firewall, consider using another protocol such as FTP.
For more information about the Forefront TMG 2010 Firewall Client and CIFS connections, please review Microsoft Knowledge Base article 913782.
New DirectAccess Blog
For anyone interested in news and information about Microsoft DirectAccess, I have started another blog at directaccess.richardhicks.com. With this blog I’ll be writing about DirectAccess in Windows Server 2008 R2, Forefront Unified Access Gateway (UAG) 2010 DirectAccess, and DirectAccess in Windows Server 2012. In addition, I’ll be touching on topics related to VPN and remote access in general, IPv6, and core networking. DirectAccess is the way of the future for managed client remote access, so I would encourage you to follow my blog and stay up to date with this wonderful technology. Of course I’ll still continue to write about edge security and Forefront TMG 2010 here, don’t worry!
IP Spoofing Alert from APIPA Address in Forefront TMG 2010
Security administrators may encounter the following IP spoofing alert on their Forefront TMG 2010 firewall:
Alert: IP Spoofing Description: Forefront TMG 2010 detected a possible spoof attack from the IP address 169.254.x.x. A spoof attack occurs when an IP address that is not reachable through the network adapter on which the packet was received. If logging for dropped packets is enabled, you can view the details of this attack in the firewall log in Forefront TMG 2010 log viewer. If the IP address belongs to a VPN client, this event may be ignored.

This alert occurs because the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall received a packet on its internal network interface from a client (server, workstation, or other host) that did not have a statically assigned IP address and was not able to obtain one from DHCP, so the client selected an IP address from the Automatic Private IP Address Assignment (APIPA) address range defined in RFC 3927.
You can safely ignore this alert, or you can resolve the issue by adding the APIPA reserved network 169.254.0.0/16 to the Internal network definition. This can be accomplished by opening the Forefront TMG 2010 management console and highlighting the Networking node in the navigation tree, then right-clicking the Internal network, selecting the Addresses tab, then clicking the Add Private button and choosing the address range 169.254.0.0 – 169.254.255.255.

Note: It is possible to resolve this issue by disabling alerts for IP spoofing attempts. However, this is considered bad security practice and is strongly discouraged.
You may recall from an earlier blog post I indicated that the best way to configure the Internal network definition in Forefront TMG 2010 is to choose the Add Adapter option. This still remains true. However, this is one of those rare cases in which you’ll want add an additional network address space to your Internal network definition to reduce the volume of IP spoofing alerts being raised by the Forefront TMG 2010 firewall.
The one side effect to implementing this change is that you will now receive a Configuration error alert informing you that your Internal network does not correlate with the network adapters that belong to it.
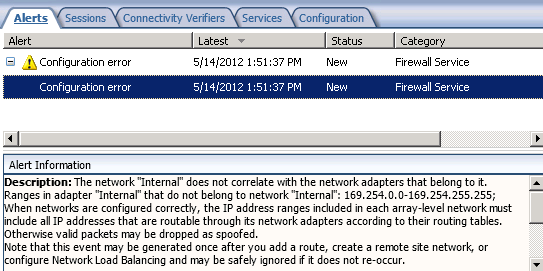
Essentially you have traded one annoying alert for another. However, the noise generated by IP spoofing alerts from clients with APIPA IP addresses might make this tradeoff worthwhile. In addition, it is much safer to disable the configuration error alert than it is the IP spoofing alert.








